Prime-boost immunization with adenoviral and modified vaccinia virus Ankara vectors enhances the durability and polyfunctionality of protective malaria CD8+ T-cell responses
- PMID: 19858306
- PMCID: PMC2798185
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00740-09
Prime-boost immunization with adenoviral and modified vaccinia virus Ankara vectors enhances the durability and polyfunctionality of protective malaria CD8+ T-cell responses
Erratum in
- Infect Immun. 2011 May;79(5):2131
Abstract
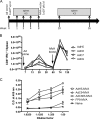
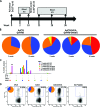
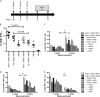
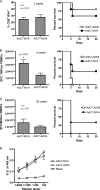
Protection against liver-stage malaria relies on the induction of high frequencies of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. We have previously reported high protective levels against mouse malaria, albeit short-lived, by a single vaccination with adenoviral vectors coding for a liver-stage antigen (ME.TRAP). Here, we report that prime-boost regimens using modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) and adenoviral vectors encoding ME.TRAP can enhance both short- and long-term sterile protection against malaria. Protection persisted for at least 6 months when simian adenoviruses AdCh63 and AdC9 were used as priming vectors. Kinetic analysis showed that the MVA boost made the adenoviral-primed T cells markedly more polyfunctional, with the number of gamma interferon (INF-gamma), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and interleukin-2 (IL-2) triple-positive and INF-gamma and TNF-alpha double-positive cells increasing over time, while INF-gamma single-positive cells declined with time. However, IFN-gamma production prevailed as the main immune correlate of protection, while neither an increase of polyfunctionality nor a high integrated mean fluorescence intensity (iMFI) correlated with protection. These data highlight the ability of optimized viral vector prime-boost regimens to generate more protective and sustained CD8+ T-cell responses, and our results encourage a more nuanced assessment of the importance of inducing polyfunctional CD8(+) T cells by vaccination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancing blood-stage malaria subunit vaccine immunogenicity in rhesus macaques by combining adenovirus, poxvirus, and protein-in-adjuvant vaccines.J Immunol. 2010 Dec 15;185(12):7583-95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001760. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21098232
-
Immune responses against a liver-stage malaria antigen induced by simian adenoviral vector AdCh63 and MVA prime-boost immunisation in non-human primates.Vaccine. 2010 Dec 16;29(2):256-65. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.10.041. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 21029806
-
Phase 1 evaluation of 3 highly immunogenic prime-boost regimens, including a 12-month reboosting vaccination, for malaria vaccination in Gambian men.J Infect Dis. 2004 Jun 15;189(12):2213-9. doi: 10.1086/421118. Epub 2004 May 24. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15181568 Clinical Trial.
-
Prime-boost vectored malaria vaccines: progress and prospects.Hum Vaccin. 2010 Jan;6(1):78-83. doi: 10.4161/hv.6.1.10116. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Hum Vaccin. 2010. PMID: 20061802 Review.
-
Progress with viral vectored malaria vaccines: A multi-stage approach involving "unnatural immunity".Vaccine. 2015 Dec 22;33(52):7444-51. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.09.094. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26476366 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity and efficacy of the novel cancer vaccine based on simian adenovirus and MVA vectors alone and in combination with PD-1 mAb in a mouse model of prostate cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016 Jun;65(6):701-13. doi: 10.1007/s00262-016-1831-8. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27052571 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Dose Intranasal ChAd Vaccine Protects Upper and Lower Respiratory Tracts against SARS-CoV-2.Cell. 2020 Oct 1;183(1):169-184.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.026. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32931734 Free PMC article.
-
ORF6 and ORF61 Expressing MVA Vaccines Impair Early but Not Late Latency in Murine Gammaherpesvirus MHV-68 Infection.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 18;10:2984. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02984. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921215 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination With Recombinant Filamentous fd Phages Against Parasite Infection Requires TLR9 Expression.Front Immunol. 2018 May 29;9:1173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01173. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29896197 Free PMC article.
-
The Threshold of Protection from Liver-Stage Malaria Relies on a Fine Balance between the Number of Infected Hepatocytes and Effector CD8+ T Cells Present in the Liver.J Immunol. 2017 Mar 1;198(5):2006-2016. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601209. Epub 2017 Jan 13. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28087668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, R. J., C. M. Hannan, S. C. Gilbert, S. M. Laidlaw, E. G. Sheu, S. Korten, R. Sinden, G. A. Butcher, M. A. Skinner, and A. V. Hill. 2004. Enhanced CD8+ T cell immune responses and protection elicited against Plasmodium berghei malaria by prime boost immunization regimens using a novel attenuated fowlpox virus. J. Immunol. 172:3094-3100. - PubMed
-
- Belnoue, E., F. T. Costa, T. Frankenberg, A. M. Vigario, T. Voza, N. Leroy, M. M. Rodrigues, I. Landau, G. Snounou, and L. Renia. 2004. Protective T cell immunity against malaria liver stage after vaccination with live sporozoites under chloroquine treatment. J. Immunol. 172:2487-2495. - PubMed
-
- Beveridge, N. E., D. A. Price, J. P. Casazza, A. A. Pathan, C. R. Sander, T. E. Asher, D. R. Ambrozak, M. L. Precopio, P. Scheinberg, N. C. Alder, M. Roederer, R. A. Koup, D. C. Douek, A. V. Hill, and H. McShane. 2007. Immunisation with BCG and recombinant MVA85A induces long-lasting, polyfunctional Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD4+ memory T lymphocyte populations. Eur. J. Immunol. 37:3089-3100. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruna-Romero, O., G. Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza, J. C. Hafalla, M. Tsuji, and R. S. Nussenzweig. 2001. Complete, long-lasting protection against malaria of mice primed and boosted with two distinct viral vectors expressing the same plasmodial antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98:11491-11496. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

