Immunotherapy of human cancers using gene modified T lymphocytes
- PMID: 19860654
- PMCID: PMC2952647
- DOI: 10.2174/156652309789753338
Immunotherapy of human cancers using gene modified T lymphocytes
Abstract
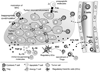
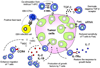
Adoptive T cell therapies can produce objective clinical responses in patients with hematologic and solid malignancies. Genetic manipulation of T lymphocytes has been proposed as a means of increasing the potency and range of this anti-tumor activity. We now review how coupling expression of transgenic receptors with countermeasures against potent tumor immune evasion strategies is proving highly effective in pre-clinical models and describe how these approaches are being evaluated in human subjects.
Figures


References
-
- Einsele H, Roosnek E, Rufer N, et al. Infusion of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T cells for the treatment of CMV infection not responding to antiviral chemotherapy. Blood. 2002;99:3916–3922. - PubMed
-
- Leen AM, Myers GD, Sili U, et al. Monoculture-derived T lymphocytes specific for multiple viruses expand and produce clinically relevant effects in immunocompromised individuals. Nat Med. 2006;12:1160–1166. - PubMed
-
- Rooney CM, Smith CA, Ng CY, et al. Infusion of cytotoxic T cells for the prevention and treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoma in allogeneic transplant recipients. Blood. 1998;92:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Heslop HE, Ng CY, Li C, et al. Long-term restoration of immunity against Epstein-Barr virus infection by adoptive transfer of gene-modified virus-specific T lymphocytes. Nat Med. 1996;2:551–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
