Plasma and urine biomarkers in acute viral hepatitis E
- PMID: 19860894
- PMCID: PMC2773234
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-7-39
Plasma and urine biomarkers in acute viral hepatitis E
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis E, caused by the hepatitis E virus (HEV), is endemic to developing countries where it manifests as waterborne outbreaks and sporadic cases. Though generally self-limited with a low mortality rate, some cases progress to fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) with high mortality. With no identified predictive or diagnostic markers, the events leading to disease exacerbation are not known. Our aim is to use proteomic tools to identify biomarkers of acute and fulminant hepatitis E.
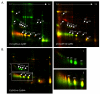
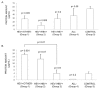
Results: We analyzed proteins in the plasma and urine of hepatitis E patients and healthy controls by two-dimensional Differential Imaging Gel Electrophoresis (DIGE) and mass spectrometry, and identified over 30 proteins to be differentially expressed during acute hepatitis E. The levels of one plasma protein, transthyretin, and one urine protein, alpha-1-microglobulin (alpha1m), were then quantitated by enzyme immunoassay (EIA) in clinical samples from a larger group of patients and controls. The results showed decreased plasma transthyretin levels (p < 0.005) and increased urine alpha1m levels (p < 0.001) in acute hepatitis E patients, compared to healthy controls. Preliminary results also showed lower urine zinc alpha glycoprotein levels in fulminant hepatitis E compared to acute disease; this remains to be confirmed with more fulminant cases.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate the utility of characterizing plasma and urine proteomes for signatures of the host response to HEV infection. We predict that plasma transthyretin and urine alpha1m could be reliable biomarkers of acute hepatitis E. Besides the utility of this approach to biomarker discovery, proteome-level changes in human biofluids would also guide towards a better understanding of host-virus interaction and disease.
Figures

References
-
- Purcell RH, Emerson SU. Hepatitis E Virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editor. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2001. pp. 3051–3062.
-
- International Committee for Taxonomy of Viruses; 2009 proposals http://talk.ictvonline.org/media/p/1194.aspx
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

