Molecular epidemiology of clade 1 influenza A viruses (H5N1), southern Indochina peninsula, 2004-2007
- PMID: 19861062
- PMCID: PMC2866389
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1510.090115
Molecular epidemiology of clade 1 influenza A viruses (H5N1), southern Indochina peninsula, 2004-2007
Abstract
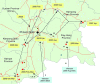
To determine the origin of influenza A virus (H5N1) epizootics in Cambodia, we used maximum-likelihood and Bayesian methods to analyze the genetic sequences of subtype H5N1 strains from Cambodia and neighboring areas. Poultry movements, rather than repeated reintroduction of subtype H5N1 viruses by wild birds, appear to explain virus circulation and perpetuation.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization/World Organisation for Animal Health/Food and Agriculture Organization H5N1 Evolution Working Group. Toward a unified nomenclature system for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N1) [conference summary]. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2008. Jul [cited 2009 Sep 14]. Available from http://www.cdc.gov/EID/content/14/7/e1.htm
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
