Poor clinical sensitivity of rapid antigen test for influenza A pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus
- PMID: 19861069
- PMCID: PMC2866420
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1510.091186
Poor clinical sensitivity of rapid antigen test for influenza A pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus
Abstract
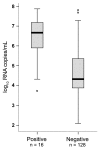
Influenza A pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus RNA was detected by reverse transcription-PCR in 144 clinical samples from Bonn, Germany. A common rapid antigen-based test detected the virus in only 11.1% of these samples. The paramount feature of rapid test-positive samples was high virus concentration. Antigen-based rapid tests appear unsuitable for virologic diagnostics in the current pandemic.
Figures
Comment in
-
Rapid antigen test for pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus.Emerg Infect Dis. 2010 May;16(5):897-8; author reply 898. doi: 10.3201/eid1605.091574. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20409404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Influenza A(H1N1)—update 59 [cited 2009 Jul 31]. Available from http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_07_27/en/index.html
-
- Robert Koch Institute. Influenza A(H1N1)—Situationseinschätzung zur Neuen Influenza [cited 2009 Jul 31]. Available from http://www.rki.de/cln_160/nn_200120/DE/Content/InfAZ/I/Influenza/IPV/Sch...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
