Structural features of the tmRNA-ribosome interaction
- PMID: 19861420
- PMCID: PMC2779675
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1584209
Structural features of the tmRNA-ribosome interaction
Abstract
Trans-translation is a process which switches the synthesis of a polypeptide chain encoded by a nonstop messenger RNA to the mRNA-like domain of a transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA). It is used in bacterial cells for rescuing the ribosomes arrested during translation of damaged mRNA and directing this mRNA and the product polypeptide for degradation. The molecular basis of this process is not well understood. Earlier, we developed an approach that allowed isolation of tmRNA-ribosomal complexes arrested at a desired step of tmRNA passage through the ribosome. We have here exploited it to examine the tmRNA structure using chemical probing and cryo-electron microscopy tomography. Computer modeling has been used to develop a model for spatial organization of the tmRNA inside the ribosome at different stages of trans-translation.
Figures

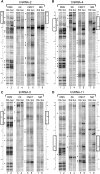
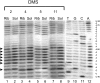
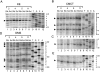

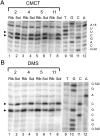

References
-
- Adrian M, Dubochet J, Lepault J, McDowall AW. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature. 1984;308:32–36. - PubMed
-
- Barends S, Wower J, Kraal B. Kinetic parameters for tmRNA binding to alanyl-tRNA synthetase and elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 2000;39:2652–2658. - PubMed
-
- Barends S, Karzai AW, Sauer RT, Wower J, Kraal B. Simultaneous and functional binding of SmpB and EF-Tu•GTP to the alanyl acceptor arm of tmRNA. J Mol Biol. 2001;314:9–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
