Interactions between neurotensin and GnRH neurons in the positive feedback control of GnRH/LH secretion in the mouse
- PMID: 19861584
- PMCID: PMC2806107
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00380.2009
Interactions between neurotensin and GnRH neurons in the positive feedback control of GnRH/LH secretion in the mouse
Abstract
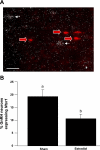
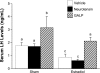
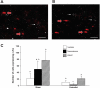
In female mammals, increased ovarian estradiol (E(2)) secretion triggers GnRH release from neurons in the basal forebrain, which drives LH secretion from the pituitary and subsequently induces ovulation. However, the neural circuits that activate this preovulatory GnRH/LH surge remain unidentified. Neurotensin is expressed in neurons of the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV), a region thought to be critical for generating the preovulatory GnRH/LH surge. E(2) induces neurotensin (Nts) gene expression in this region, and blockade of neurotensin signaling reduces the LH surge in the rat. We postulated that neurotensin signaling plays a similar role in generating the E(2)-induced GnRH/LH surge in mice. We used in situ hybridization (ISH) to determine whether E(2) induces Nts expression in the mouse and found evidence to support this proposition. Next, we determined that the neurotensin receptor (Ntsr2) is present in many GnRH-expressing neurons. Since the kisspeptin gene (Kiss1) is expressed in the AVPV and is responsive to E(2), we predicted that some neurons in this region express both Kiss1 and Nts; however, by double-label ISH, we observed no coexpression of the two mRNAs. We also postulated that Nts mRNA expression would increase in parallel with the E(2)-induced LH surge and that the central (icv) administration of neurotensin would stimulate LH secretion and activation of GnRH neurons but found no evidence to support either of these hypotheses. Together, these findings suggest that, although neurotensin neurons in the AVPV are targets for regulation by E(2), neurotensin does not appear to play a direct role in generating the GnRH/LH surge in the mouse.
Figures


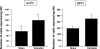


References
-
- Akema T, Praputpittaya C, Kimura F. Effects of preoptic microinjection of neurotensin on luteinizing hormone secretion in unanesthetized ovariectomized rats with or without estrogen priming. Neuroendocrinology 46: 345–349, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Alexander MJ, Dobner PR, Miller MA, Bullock BP, Dorsa DM, Leeman SE. Estrogen induces neurotensin/neuromedin N messenger ribonucleic acid in a preoptic nucleus essential for the preovulatory surge of luteinizing hormone in the rat. Endocrinology 125: 2111–2117, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Alexander MJ, Kiraly ZJ, Leeman SE. Sexually dimorphic distribution of neurotensin/neuromedin N mRNA in the rat preoptic area. J Comp Neurol 311: 84–96, 1991 - PubMed
-
- Alexander MJ, Mahoney PD, Ferris CF, Carraway RE, Leeman SE. Evidence that neurotensin participates in the central regulation of the preovulatory surge of luteinizing hormone in the rat. Endocrinology 124: 783–788, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Bronson FH, Vom Saal FS. Control of the preovulatory release of luteinizing hormone by steroids in the mouse. Endocrinology 104: 1247–1255, 1979 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

