Crystal structure of glucagon-like peptide-1 in complex with the extracellular domain of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- PMID: 19861722
- PMCID: PMC2804221
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.033829
Crystal structure of glucagon-like peptide-1 in complex with the extracellular domain of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
Abstract
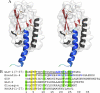
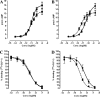
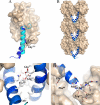
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) is an incretin released from intestinal L-cells in response to food intake. Activation of the GLP-1 receptor potentiates the synthesis and release of insulin from pancreatic beta-cells in a glucose-dependent manner. The GLP-1 receptor belongs to class B of the G-protein-coupled receptors, a subfamily characterized by a large N-terminal extracellular ligand binding domain. Exendin-4 and GLP-1 are 50% identical, and exendin-4 is a full agonist with similar affinity and potency for the GLP-1 receptor. We recently solved the crystal structure of the GLP-1 receptor extracellular domain in complex with the competitive antagonist exendin-4(9-39). Interestingly, the isolated extracellular domain binds exendin-4 with much higher affinity than the endogenous agonist GLP-1. Here, we have solved the crystal structure of the extracellular domain in complex with GLP-1 to 2.1 Aresolution. The structure shows that important hydrophobic ligand-receptor interactions are conserved in agonist- and antagonist-bound forms of the extracellular domain, but certain residues in the ligand-binding site adopt a GLP-1-specific conformation. GLP-1 is a kinked but continuous alpha-helix from Thr(13) to Val(33) when bound to the extracellular domain. We supplemented the crystal structure with site-directed mutagenesis to link the structural information of the isolated extracellular domain with the binding properties of the full-length receptor. The data support the existence of differences in the binding modes of GLP-1 and exendin-4 on the full-length GLP-1 receptor.
Figures
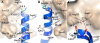

References
-
- Mojsov S., Heinrich G., Wilson I. B., Ravazzola M., Orci L., Habener J. F. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 11880–11889 - PubMed
-
- Schmidt W. E., Siegel E. G., Creutzfeldt W. (1985) Diabetologia 28, 704–707 - PubMed
-
- Orskov C., Holst J. J., Nielsen O. V. (1988) Endocrinology 123, 2009–2013 - PubMed
-
- Wettergren A., Schjoldager B., Mortensen P. E., Petersen H., Ørskov C., Holst J. J. (1993) Digestion 54, 384–385
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

