Tumour-targeted delivery of TRAIL using Salmonella typhimurium enhances breast cancer survival in mice
- PMID: 19861961
- PMCID: PMC2778534
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605403
Tumour-targeted delivery of TRAIL using Salmonella typhimurium enhances breast cancer survival in mice
Abstract
Background: An effective cancer therapeutic must selectively target tumours with minimal systemic toxicity. Expression of a cytotoxic protein using Salmonella typhimurium would enable spatial and temporal control of delivery because these bacteria preferentially target tumours over normal tissue.
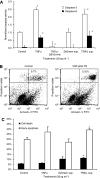
Methods: We engineered non-pathogenic S. typhimurium to secrete murine TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) under the control of the prokaryotic radiation-inducible RecA promoter. The response of the RecA promoter to radiation was measured using fluorometry and immunoblotting. TRAIL toxicity was determined using flow cytometry and by measuring caspase-3 activation. A syngeneic murine tumour model was used to determine bacterial accumulation and the response to expressed TRAIL.
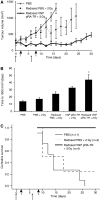
Results: After irradiation, engineered S. typhimurium secreted TRAIL, which caused caspase-3-mediated apoptosis and death in 4T1 mammary carcinoma cells in culture. Systemic injection of Salmonella and induction of TRAIL expression using 2 Gy gamma-irradiation caused a significant delay in mammary tumour growth and reduced the risk of death by 76% when compared with irradiated controls. Repeated dosing with TRAIL-bearing Salmonella in conjunction with radiation improved the 30-day survival from 0 to 100%.
Conclusion: These results show the pre-clinical utility of S. typhimurium as a TRAIL expression vector that effectively reduces tumour growth and extends host survival.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson DG, Kowalczykowski SC (1998) Reconstitution of an SOS response pathway: derepression of transcription in response to DNA breaks. Cell 95: 975–979 - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert A, DeForge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 104: 155–162 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbe S, Van Mellaert L, Theys J, Geukens N, Lammertyn E, Lambin P, Anne J (2005) Secretory production of biologically active rat interleukin-2 by Clostridium acetobutylicum DSM792 as a tool for anti-tumor treatment. FEMS Microbiol Lett 246: 67–73 - PubMed
-
- Beg AA, Baltimore D (1996) An essential role for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science 274: 782–784 - PubMed
-
- Belka C, Jendrossek V, Pruschy M, Vink S, Verheij M, Budach W (2004) Apoptosis-modulating agents in combination with radiotherapy-current status and outlook. Int J Radiat Oncol, Biol, Phys 58: 542–554 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

