Multiple loci influence erythrocyte phenotypes in the CHARGE Consortium
- PMID: 19862010
- PMCID: PMC2778265
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.466
Multiple loci influence erythrocyte phenotypes in the CHARGE Consortium
Abstract
Measurements of erythrocytes within the blood are important clinical traits and can indicate various hematological disorders. We report here genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for six erythrocyte traits, including hemoglobin concentration (Hb), hematocrit (Hct), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) and red blood cell count (RBC). We performed an initial GWAS in cohorts of the CHARGE Consortium totaling 24,167 individuals of European ancestry and replication in additional independent cohorts of the HaemGen Consortium totaling 9,456 individuals. We identified 23 loci significantly associated with these traits in a meta-analysis of the discovery and replication cohorts (combined P values ranging from 5 x 10(-8) to 7 x 10(-86)). Our findings include loci previously associated with these traits (HBS1L-MYB, HFE, TMPRSS6, TFR2, SPTA1) as well as new associations (EPO, TFRC, SH2B3 and 15 other loci). This study has identified new determinants of erythrocyte traits, offering insight into common variants underlying variation in erythrocyte measures.
Figures
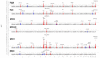
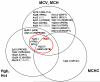
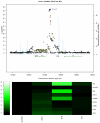
Comment in
-
Genes determining blood cell traits.Nat Genet. 2009 Nov;41(11):1161-2. doi: 10.1038/ng1109-1161. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19862006 No abstract available.
References
-
- Havlik RJ, et al. Evidence for additional blood pressure correlates in adults 20-56 years old. Circulation. 1980;61:710–5. - PubMed
-
- Tell GS, et al. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS) Collaborative Research Group Correlates of blood pressure in community-dwelling older adults. Hypertension. 1994;23:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Zakai NA, et al. A prospective study of anemia status, hemoglobin concentration, and mortality in an elderly cohort: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:2214–20. - PubMed
-
- Whitfield JB, Martin NG. Genetic and environmental influences on the size and number of cells in the blood. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2:133–44. - PubMed
-
- Evans DM, Frazer IH, Martin NG. Genetic and environmental causes of variation in basal levels of blood cells. Twin Res. 1999;2:250–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

