Subtypes of functional alpha1-adrenoceptor
- PMID: 19862476
- PMCID: PMC11115521
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0174-4
Subtypes of functional alpha1-adrenoceptor
Abstract
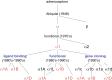
In this review, subtypes of functional alpha1-adrenoceptor are discussed. These are cell membrane receptors, belonging to the seven-transmembrane-spanning G-protein-linked family of receptors, which respond to the physiological agonist noradrenaline. alpha1-Adrenoceptors can be divided into alpha1A-, alpha1B- and alpha1D-adrenoceptors, all of which mediate contractile responses involving Gq/11 and inositol phosphate turnover. A fourth alpha1-adrenoceptor, the alpha1L-, represents a functional phenotype of the alpha1A-adrenoceptor. alpha1-Adrenoceptor subtype knock-out mice have refined our knowledge of the functions of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes, particuarly as subtype-selective agonists and antagonists are not available for all subtypes. alpha1-Adrenoceptors function as stimulatory receptors involved particularly in smooth muscle contraction, especially contraction of vascular smooth muscle, both in local vasoconstriction and in the control of blood pressure and temperature, and contraction of the prostate and bladder neck. Central actions are now being elucidated.
Figures
References
-
- Ahlquist RP. A study of the adrenotropic receptors. Am J Physiol. 1948;153:586–600. - PubMed
-
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. - PubMed
-
- Starke K, Langer SZ. A note on the terminology for presynaptic receptors. In: Langer SZ, Starke K, Dubocovich ML, editors. Presynaptic receptors. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1979. pp. 1–3.
-
- Morrow AL, Creese I. Characterization of alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a re-evaluation of [3H]WB4101 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986;29:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Han C, Abel PW, Minneman KP. Alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987;329:333–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

