The tetracycline resistome
- PMID: 19862477
- PMCID: PMC11115633
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0172-6
The tetracycline resistome
Abstract
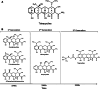
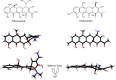
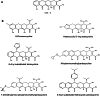
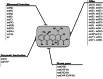
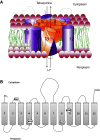
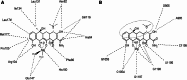
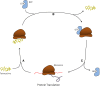
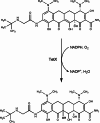
Resistance to tetracycline emerged soon after its discovery six decades ago. Extensive clinical and non-clinical uses of this class of antibiotic over the years have combined to select for a large number of resistant determinants, collectively termed the tetracycline resistome. In order to impart resistance, microbes use different molecular mechanisms including target protection, active efflux, and enzymatic degradation. A deeper understanding of the structure, mechanism, and regulation of the genes and proteins associated with tetracycline resistance will contribute to the development of tetracycline derivatives that overcome resistance. Newer generations of tetracyclines derived from engineering of biosynthetic genetic programs, semi-synthesis, and in particular recent developments in their chemical synthesis, together with a growing understanding of resistance, will serve to retain this class of antibiotic to combat pathogens.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

