RAD51 paralogs promote homology-directed repair at diversifying immunoglobulin V regions
- PMID: 19863810
- PMCID: PMC2774322
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-98
RAD51 paralogs promote homology-directed repair at diversifying immunoglobulin V regions
Abstract
Background: Gene conversion depends upon the same factors that carry out more general process of homologous recombination, including homologous gene targeting and recombinational repair. Among these are the RAD51 paralogs, conserved factors related to the key recombination factor, RAD51. In chicken and other fowl, gene conversion (templated mutation) diversifies immunoglobulin variable region sequences. This allows gene conversion and recombinational repair to be studied using the chicken DT40 B cell line, which carries out constitutive gene conversion and provides a robust and physiological model for homology-directed repair in vertebrate cells.
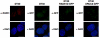
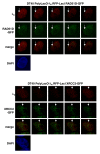
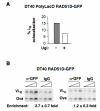
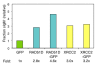
Results: We show that DT40 contains constitutive nuclear foci of the repair factors RAD51D and XRCC2, consistent with activated homologous recombination. Single-cell imaging of a DT40 derivative in which the rearranged and diversifying immunoglobulin lambdaR light chain gene is tagged with polymerized lactose operator, DT40 PolyLacO-lambdaR, showed that RAD51D and XRCC2 localize to the diversifying lambdaR gene. Colocalizations correlate both functionally and physically with active immunoglobulin gene conversion. Ectopic expression of either RAD51D or XRCC2 accelerated the clonal rate of gene conversion, and conversion tracts were significantly longer in RAD51D than XRCC2 transfectants.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate direct functions of RAD51D and XRCC2 in immunoglobulin gene conversion, and also suggest that modulation of levels of repair factors may be a useful strategy to promote gene correction in other cell types.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Brca1 in immunoglobulin gene conversion and somatic hypermutation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Feb 1;7(2):253-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.10.002. Epub 2007 Nov 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18036997 Free PMC article.
-
Similar effects of Brca2 truncation and Rad51 paralog deficiency on immunoglobulin V gene diversification in DT40 cells support an early role for Rad51 paralogs in homologous recombination.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(3):1124-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1124-1134.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657438 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of XRCC2/3 transforms immunoglobulin V gene conversion into somatic hypermutation.Nature. 2001 Aug 30;412(6850):921-6. doi: 10.1038/35091100. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11528482
-
Gene conversion in the chicken immunoglobulin locus: a paradigm of homologous recombination in higher eukaryotes.Experientia. 1994 Mar 15;50(3):270-6. doi: 10.1007/BF01924010. Experientia. 1994. PMID: 8143801 Review.
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase-mediated hypermutation in the DT40 cell line.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Mar 12;364(1517):639-44. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0202. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19008193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic diversification by somatic gene conversion.Genes (Basel). 2011 Jan 10;2(1):48-58. doi: 10.3390/genes2010048. Genes (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24710138 Free PMC article.
-
Diversification of immunoglobulin genes by gene conversion in the domestic chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus).Discov Immunol. 2023 Jan 19;2(1):kyad002. doi: 10.1093/discim/kyad002. eCollection 2023. Discov Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38567069 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted gene therapies: tools, applications, optimization.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 May-Jun;47(3):264-81. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2012.658112. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22530743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody discovery ex vivo accelerated by the LacO/LacI regulatory network.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036032. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558313 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

