Analysis and comparison of very large metagenomes with fast clustering and functional annotation
- PMID: 19863816
- PMCID: PMC2774329
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-359
Analysis and comparison of very large metagenomes with fast clustering and functional annotation
Abstract
Background: The remarkable advance of metagenomics presents significant new challenges in data analysis. Metagenomic datasets (metagenomes) are large collections of sequencing reads from anonymous species within particular environments. Computational analyses for very large metagenomes are extremely time-consuming, and there are often many novel sequences in these metagenomes that are not fully utilized. The number of available metagenomes is rapidly increasing, so fast and efficient metagenome comparison methods are in great demand.
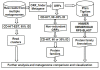
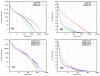
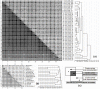
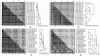
Results: The new metagenomic data analysis method Rapid Analysis of Multiple Metagenomes with a Clustering and Annotation Pipeline (RAMMCAP) was developed using an ultra-fast sequence clustering algorithm, fast protein family annotation tools, and a novel statistical metagenome comparison method that employs a unique graphic interface. RAMMCAP processes extremely large datasets with only moderate computational effort. It identifies raw read clusters and protein clusters that may include novel gene families, and compares metagenomes using clusters or functional annotations calculated by RAMMCAP. In this study, RAMMCAP was applied to the two largest available metagenomic collections, the "Global Ocean Sampling" and the "Metagenomic Profiling of Nine Biomes".
Conclusion: RAMMCAP is a very fast method that can cluster and annotate one million metagenomic reads in only hundreds of CPU hours. It is available from http://tools.camera.calit2.net/camera/rammcap/.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of k-mer spectrum applicability for metagenomic dissimilarity analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jan 16;17:38. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0875-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26774270 Free PMC article.
-
COGNIZER: A Framework for Functional Annotation of Metagenomic Datasets.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 11;10(11):e0142102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142102. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26561344 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the composition of species in metagenomes by clustering of next-generation read sequences.Methods. 2014 Oct 1;69(3):213-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.07.009. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Methods. 2014. PMID: 25072168
-
Assessment of metagenomic assemblers based on hybrid reads of real and simulated metagenomic sequences.Brief Bioinform. 2020 May 21;21(3):777-790. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz025. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30860572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Web Resources for Metagenomics Studies.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015 Oct;13(5):296-303. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26602607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assembling bacterial puzzles: piecing together functions into microbial pathways.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Aug 24;6(3):lqae109. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae109. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39184378 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Consortium Associated with the Antarctic Marine Ciliate Euplotes focardii: An Investigation from Genomic Sequences.Microb Ecol. 2015 Aug;70(2):484-97. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0568-9. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Microb Ecol. 2015. PMID: 25704316 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic approaches for functional annotation and pathway inference in metagenomics data.Brief Bioinform. 2012 Nov;13(6):696-710. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs070. Brief Bioinform. 2012. PMID: 23175748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salinity and Time Can Alter Epibacterial Communities of an Invasive Seaweed.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 15;10:2870. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02870. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32010064 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional response of microbial communities in thawing Alaskan permafrost soils.Front Microbiol. 2015 Mar 16;6:197. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00197. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25852660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeLong EF, Preston CM, Mincer T, Rich V, Hallam SJ, Frigaard NU, Martinez A, Sullivan MB, Edwards R, Brito BR, et al. Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean's interior. Science. 2006;311:496–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

