Reductions in laminin beta2 mRNA translation are responsible for impaired IGFBP-5-mediated mesangial cell migration in the presence of high glucose
- PMID: 19864299
- PMCID: PMC2822519
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00483.2009
Reductions in laminin beta2 mRNA translation are responsible for impaired IGFBP-5-mediated mesangial cell migration in the presence of high glucose
Abstract
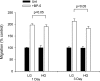
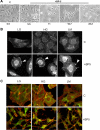
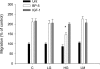
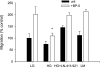
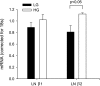
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) mediates mesangial cell migration through activation of cdc42, and laminin421 binding to alpha(6)beta(1)-integrin (Berfield AK, Hansen KM, Abrass CK. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291: C589-C599, 2006). Because glomerular expression of laminin beta(2) is reduced in diabetic rats (Abrass CK, Spicer D, Berfield AK, St. John PL, Abrahamson DR. Am J Pathol 151: 1131-1140, 1997), we directly examined the effect of hyperglycemia on mesangial cell migration and laminin beta2 expression. Migration mediated by IGFBP-5 is impaired in the presence of 25 mM glucose. This reduction in migration was found to result from a loss in mesangial cell synthesis of laminin421, and IGFBP-5-induced migration could be restored by replacing laminin421. Additional studies showed that there was selective reduction in mRNA translation of laminin beta2 in the presence of high glucose. Preserved synthesis of laminin beta1 indicates that not all proteins are reduced by high glucose and confirms prior data showing that laminin411 cannot substitute for laminin421 in IGFBP-5-mediated migration. Given the importance of mesangial migration in the reparative response to diabetes-associated mesangiolysis, these findings provide new insights into abnormalities associated with diabetic nephropathy and the potential importance of differential control of protein translation in determination of alterations of protein expression.
Figures

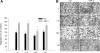
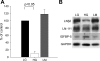

References
-
- Abrass CK, Berfield AK, Andress DL. Heparin binding domain of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 stimulates mesangial cell migration. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 273: F899–F906, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Abrass CK, Spicer D, Raugi GJ. Insulin induces a change in extracellular matrix glycoproteins synthesized by rat mesangial cells in culture. Kidney Int 46: 613–620, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Abrass CK, Spicer D, Raugi GJ. Induction of nodular sclerosis by insulin in rat mesangial cells in vitro: studies of collagen. Kidney Int 47: 25–37, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

