Chemokine-like receptor-1 expression by central nervous system-infiltrating leukocytes and involvement in a model of autoimmune demyelinating disease
- PMID: 19864606
- PMCID: PMC2904075
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803435
Chemokine-like receptor-1 expression by central nervous system-infiltrating leukocytes and involvement in a model of autoimmune demyelinating disease
Abstract
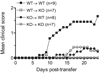
We examined the involvement of chemokine-like receptor-1 (CMKLR1) in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model of human multiple sclerosis. Upon EAE induction by active immunization with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein amino acids 35-55 (MOG(35-55)), microglial cells and CNS-infiltrating myeloid dendritic cells expressed CMKLR1, as determined by flow cytometric analysis. In addition, chemerin, a natural ligand for CMKLR1, was up-regulated in the CNS of mice with EAE. We found that CMKLR1-deficient (CMKLR1 knockout (KO)) mice develop less severe clinical and histologic disease than their wild-type (WT) counterparts. CMKLR1 KO lymphocytes proliferate and produce proinflammatory cytokines in vitro, yet MOG(35-55)-reactive CMKLR1 KO lymphocytes are deficient in their ability to induce EAE by adoptive transfer to WT or CMKLR1 KO recipients. Moreover, CMKLR1 KO recipients fail to fully support EAE induction by transferred MOG-reactive WT lymphocytes. The results imply involvement of CMKLR1 in both the induction and effector phases of disease. We conclude that CMKLR1 participates in the inflammatory mechanisms of EAE and represents a potential therapeutic target in multiple sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
B.A.Z. has received salary and stock options from ChemoCentryx. All other authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Steinman L. Multiple sclerosis: a two-stage disease. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:762–764. - PubMed
-
- Yednock T, Cannon C, Fritz L, Sanchez-Madrid F, Steinman L, Karin N. Prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by antibodies against α4β1 integrin. Nature. 1992;356:63–66. - PubMed
-
- Rudick RA, Stuart WH, Calabresi PA, Confavreux C, Galetta SL, Radue E-W, Lublin FD, Weinstock-Guttman B, Wynn DR, Lynn F, et al. Natalizumab plus interferon β-1a for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:911–923. - PubMed
-
- Karpus WJ, Ransohoff RM. Chemokine regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: temporal and spatial expression patterns govern disease pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 1998;161:2667–2671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007290/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM037734/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI047822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-59635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL-67674/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI-47822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI059635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL067674/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM037734/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL067674/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM-37734/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079320/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-079320/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI047822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

