A homozygous CARD9 mutation in a family with susceptibility to fungal infections
- PMID: 19864672
- PMCID: PMC2793117
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810719
A homozygous CARD9 mutation in a family with susceptibility to fungal infections
Abstract
Background: Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis may be manifested as a primary immunodeficiency characterized by persistent or recurrent infections of the mucosa or the skin with candida species. Most cases are sporadic, but both autosomal dominant inheritance and autosomal recessive inheritance have been described.
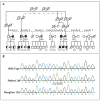
Methods: We performed genetic studies in 36 members of a large, consanguineous five-generation family, in which 4 members had recurrent fungal infections and an additional 3 members died during adolescence, 2 after invasive infection of the brain with candida species. All 36 family members were enrolled in the study, and 22 had blood samples taken for DNA analysis. Homozygosity mapping was used to locate the mutated gene. In the 4 affected family members (patients) and the 18 unaffected members we sequenced CARD9, the gene encoding the caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 9, carried out T-cell phenotyping, and performed functional studies, with the use of either leukocytes from the patients or a reconstituted murine model of the genetic defect.
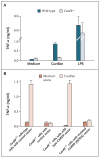
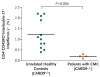
Results: We found linkage (lod score, 3.6) to a genomic interval on chromosome 9q, including CARD9. All four patients had a homozygous point mutation in CARD9, resulting in a premature termination codon (Q295X). Healthy family members had wild-type expression of the CARD9 protein; the four patients lacked wild-type expression, which was associated with low numbers of Th17 cells (helper T cells producing interleukin-17). Functional studies based on genetic reconstitution of myeloid cells from Card9(-/-) mice showed that the Q295X mutation impairs innate signaling from the antifungal pattern-recognition receptor dectin-1.
Conclusions: An autosomal recessive form of susceptibility to chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis is associated with homozygous mutations in CARD9.
2009 Massachusetts Medical Society
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Yeast infections--human genetics on the rise.N Engl J Med. 2009 Oct 29;361(18):1798-801. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe0907186. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19864679 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kirkpatrick CH. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:197–206. - PubMed
-
- Lilic D. New perspectives on the immunology of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2002;15:143–7. - PubMed
-
- Eggimann P, Garbino J, Pittet D. Epidemiology of Candida species infections in critically ill non-immunosuppressed patients. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:685–702. - PubMed
-
- Drouhet E, Dupont B. Chronic mucocutaneous candidosis and other superficial and systemic mycoses successfully treated with ketoconazole. Rev Infect Dis. 1980;2:606–19. - PubMed
-
- Kauffman CA, Shea MJ, Frame PT. Invasive fungal infections in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Arch Intern Med. 1981;141:1076–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
