Cleaved high molecular weight kininogen inhibits tube formation of endothelial progenitor cells via suppression of matrix metalloproteinase 2
- PMID: 19874467
- PMCID: PMC3142619
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03662.x
Cleaved high molecular weight kininogen inhibits tube formation of endothelial progenitor cells via suppression of matrix metalloproteinase 2
Abstract
Background and objective: Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) contribute to postnatal neovascularization, thus promoting wide interest in their therapeutic potential in vascular injury and prevention of their dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Cleaved high molecular weight kininogen (HKa), an activation product of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system (KKS), inhibits the functions of differentiated endothelial cells including in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis. In this study, our results provided the first evidence that HKa is able to target EPCs and inhibits their tube forming capacity.
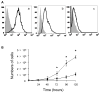
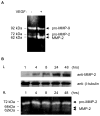
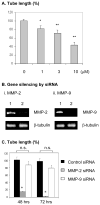
Methods and results: We determined the effect of HKa on EPCs using a three-dimensional vasculogenesis assay. Upon stimulation with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) alone, EPCs formed vacuoles and tubes, and differentiated into capillary-like networks. As detected by gelatinolytic activity assay, VEGF stimulated secretion and activation of matrix metallopeptidase 2 (MMP-2), but not MMP-9, in the conditioned medium of 3D culture of EPCs. Specific inhibition or gene ablation of MMP-2, but not MMP-9, blocked the vacuole and tube formation by EPCs. Thus, MMP-2 is selectively required for EPC vasculogenesis. In a concentration-dependent manner, HKa significantly inhibited tube formation by EPCs and the conversion of pro-MMP-2 to MMP-2. Moreover, HKa completely blocked the association between pro-MMP-2 and alphavbeta3 integrin, and its inhibition of MMP-2 activation was dependent on the presence of alphavbeta3 integrin. In a purified system, HKa did not directly inhibit MMP-2 activity.
Conclusions: HKa inhibits tube forming capacity of EPCs by suppression of MMP-2 activation, which may constitute a novel link between activation of the KKS and EPC dysfunction.
Figures




References
-
- Prater DN, Case J, Ingram DA, Yoder MC. Working hypothesis to redefine endothelial progenitor cells. Leukemia. 2007;21:1141–9. - PubMed
-
- Werner N, Nickenig G. Endothelial progenitor cells in health and atherosclerotic disease. Annals of Medicine. 2007;39:82–90. - PubMed
-
- Melero-Martin JM, Khan ZA, Picard A, Wu X, Paruchuri S, Bischoff J. In vivo vasculogenic potential of human blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Blood. 2007;109:4761–8. - PubMed
-
- Colman RW, Schmaier AH. Contact System: A Vascular Biology Modulator With Anticoagulant, Profibrinolytic, Antiadhesive, and Proinflammatory Attributes. Blood. 1997;90:3819–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

