Mechanisms of ubiquitin transfer by the anaphase-promoting complex
- PMID: 19874575
- PMCID: PMC2790831
- DOI: 10.1186/jbiol184
Mechanisms of ubiquitin transfer by the anaphase-promoting complex
Abstract
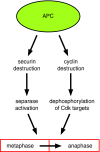
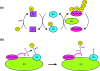
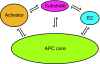
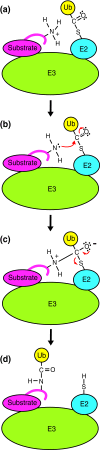
The anaphase-promoting complex (APC) is a ubiquitin-protein ligase required for the completion of mitosis in all eukaryotes. Recent mechanistic studies reveal how this remarkable enzyme combines specificity in substrate binding with flexibility in ubiquitin transfer, thereby allowing the modification of multiple lysines on the substrate as well as specific lysines on ubiquitin itself.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Substrate-specific regulation of ubiquitination by the anaphase-promoting complex.Cell Cycle. 2011 Jan 1;10(1):52-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.1.14387. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21191176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Doc1 subunit is a processivity factor for the anaphase-promoting complex.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;4(11):880-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb871. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12402045
-
The anaphase-promoting complex: a key factor in the regulation of cell cycle.Oncogene. 2005 Jan 13;24(3):314-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207973. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15678131 Review.
-
UBE2S drives elongation of K11-linked ubiquitin chains by the anaphase-promoting complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 26;107(4):1355-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912802107. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080579 Free PMC article.
-
The anaphase-promoting complex: new subunits and regulators.Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:583-609. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.583. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10872461 Review.
Cited by
-
The phylogenomic analysis of the anaphase promoting complex and its targets points to complex and modern-like control of the cell cycle in the last common ancestor of eukaryotes.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Sep 23;11:265. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-265. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21943402 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubp15 deubiquitinase promotes timely entry into S phase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Jun 15;26(12):2205-16. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-09-1400. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25877870 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate binding on the APC/C occurs between the coactivator Cdh1 and the processivity factor Doc1.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jan;18(1):6-13. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1979. Epub 2010 Dec 26. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21186364 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of APC/C-Cdh1 and its function in neuronal survival.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Dec;46(3):547-54. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8309-2. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22836916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of the APC/C: organization, function, and structure.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;46(2):118-36. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.541420. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21261459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

