PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro
- PMID: 19874578
- PMCID: PMC2790859
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2419
PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro
Abstract
Introduction: Alterations in cell cycle regulators have been implicated in human malignancies including breast cancer. PD 0332991 is an orally active, highly selective inhibitor of the cyclin D kinases (CDK)4 and CDK6 with ability to block retinoblastoma (Rb) phosphorylation in the low nanomolar range. To identify predictors of response, we determined the in vitro sensitivity to PD 0332991 across a panel of molecularly characterized human breast cancer cell lines.
Methods: Forty-seven human breast cancer and immortalized cell lines representing the known molecular subgroups of breast cancer were treated with PD 0332991 to determine IC50 values. These data were analyzed against baseline gene expression data to identify genes associated with PD 0332991 response.
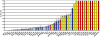
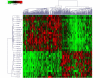
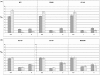
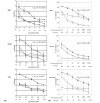
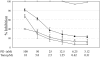
Results: Cell lines representing luminal estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) subtype (including those that are HER2 amplified) were most sensitive to growth inhibition by PD 0332991 while nonluminal/basal subtypes were most resistant. Analysis of variance identified 450 differentially expressed genes between sensitive and resistant cells. pRb and cyclin D1 were elevated and CDKN2A (p16) was decreased in the most sensitive lines. Cell cycle analysis showed G0/G1 arrest in sensitive cell lines and Western blot analysis demonstrated that Rb phosphorylation is blocked in sensitive lines but not resistant lines. PD 0332991 was synergistic with tamoxifen and trastuzumab in ER+ and HER2-amplified cell lines, respectively. PD 0332991 enhanced sensitivity to tamoxifen in cell lines with conditioned resistance to ER blockade.
Conclusions: These studies suggest a role for CDK4/6 inhibition in some breast cancers and identify criteria for patient selection in clinical studies of PD 0332991
Figures

References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, Rijn M van de, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschilkov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, Rijn M van de, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lonning P, Borresen-Dale AL. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sotiriou C, Neo SY, McShane LM, Korn EL, Long PM, Jazaeri A, Martiat P, Fox SB, Harris AL, Liu ET. Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:10393–10398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1732912100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

