Strain differences in the distribution of N-methyl-d-aspartate and gamma (gamma)-aminobutyric acid-A receptors in rat brain
- PMID: 19874829
- PMCID: PMC2810679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.10.010
Strain differences in the distribution of N-methyl-d-aspartate and gamma (gamma)-aminobutyric acid-A receptors in rat brain
Abstract
Aims: Previous studies have shown that the Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rat strain exhibits depressive symptoms such as anhedonia, psychomotor retardation, ambivalence and negative memory bias following exposure to stress. Given the involvement of excitatory glutamate and inhibitory gamma (gamma)-aminobutyric acid (GABA) signaling pathways in influencing depressive behavior, the present study investigated strain differences in the distribution of central N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and GABA(A) receptor sites in WKY compared to their inbred counterpart, Wistar (WIS) rats.
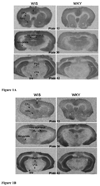
Main methods: Quantitative autoradiographic analysis was used to map the binding and distribution of NMDA and GABA(A) receptors in various brain regions in WKY and WIS rats.
Key findings: Results indicated a significant difference between the two strains. Lower NMDA receptor binding was found in the anterior cingulate cortex, caudate putmen, nucleus accumbens, CA1 region of the hippocampus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata in WKY compared to WIS rats. Conversely, higher GABA(A) receptor binding was found in the amygdala, caudate putmen, dentate gyrus, CA2 and CA3 fields of the hippocampus, periaqueductal grey and substantia nigra pars reticulata in WKY compared to WIS rats.
Significance: Given that these two rat strains differ in their behavioural, endocrine and neurochemical profile, the observed strain differences in NMDA and GABA(A) receptor binding suggest that these two neurotransmitter systems may be involved in the depressive and stress-sensitive phenotype of the WKY rat strain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptors are altered by stress and alcohol in Wistar-Kyoto rat brain.Neuroscience. 2010 Aug 11;169(1):125-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May 11. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20466039 Free PMC article.
-
Functional neuroanatomy of the nigrostriatal and striatonigral pathways as studied with dual probe microdialysis in the awake rat--II. Evidence for striatal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor regulation of striatonigral GABAergic transmission and motor function.Neuroscience. 1996 May;72(1):89-97. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00556-0. Neuroscience. 1996. PMID: 8730708
-
Genetically determined differences in noradrenergic function: The spontaneously hypertensive rat model.Brain Res. 2016 Jun 15;1641(Pt B):291-305. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.11.019. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26612520
-
Strain differences in the distribution of dopamine transporter sites in rat brain.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003 Sep;27(6):913-9. doi: 10.1016/S0278-5846(03)00150-7. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 14499307
-
Strain differences in the expression of dopamine D1 receptors in Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) and Wistar rats.Life Sci. 2008 Jul 4;83(1-2):74-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 May 24. Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18558411 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dysfunctional inhibitory mechanisms in locus coeruleus neurons of the wistar kyoto rat.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Jan 13;18(7):pyu122. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu122. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25586927 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of aging and genotype on NMDA receptor expression in growth hormone receptor knockout (GHRKO) mice.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011 Jun;66(6):607-19. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glr024. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21459761 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal NMDA receptor activation constrains inactivity-induced phrenic motor facilitation in Charles River Sprague-Dawley rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Oct 1;117(7):682-93. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00342.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 25103979 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-related differences after experimental traumatic brain injury in rats.J Neurotrauma. 2010 Jul;27(7):1243-53. doi: 10.1089/neu.2010.1270. J Neurotrauma. 2010. PMID: 20392137 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant-like effects of low ketamine dose is associated with increased hippocampal AMPA/NMDA receptor density ratio in female Wistar-Kyoto rats.Neuroscience. 2012 Jun 28;213:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.052. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22521815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altamura CA, Mauri MC, Ferrara A, Moro AR, Andrea G, Zamberlan F. Plasma and platelet excitatory amino acids in psychiatric disorders. American Journal of Psychology. 1993;150:1731–1733. - PubMed
-
- Auer DP, Putz B, Kraft E, Lipinski B, Schill J, Holsboer F. Reduced glutamate in the anterior cingulate cortex in depression: an in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Biological Psychiatry. 2000;47:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Bagdy E, Kiraly I, Harsing LGJ. Reciprocal innervation between serotonergic and GABAergic neurons in raphe nuclei of the rat. Neurochemical Research. 2000;25(11):1465–1473. - PubMed
-
- Banks MI, White JA, Pearce RA. Interactions between distinct GABA (A) circuits in hippocampus. Neuron. 2000;25(2):449–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous