Incretin-based therapies: viewpoints on the way to consensus
- PMID: 19875556
- PMCID: PMC2811437
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-S315
Incretin-based therapies: viewpoints on the way to consensus
Figures
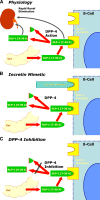
References
-
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA: The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006; 368: 1696– 1705 - PubMed
-
- Nauck MA, Heimesaat MM, Behle K, Holst JJ, Nauck MS, Ritzel R, Hüfner M, Schmiegel WH: Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on counterregulatory hormone responses, cognitive functions, and insulin secretion during hyperinsulinemic, stepped hypoglycemic clamp experiments in healthy volunteers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 1239– 1246 - PubMed
-
- Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ: Minireview: glucagon-like peptides regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in the pancreas, gut, and central nervous system. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 2653– 2659 - PubMed
-
- Wettergren A, Schjoldager B, Mortensen PE, Myhre J, Christiansen J, Holst JJ: Truncated GLP-1 (proglucagon 78-107-amide) inhibits gastric and pancreatic functions in man. Dig Dis Sci 1993; 38: 665– 673 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

