Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-specific AKT1 is oncogenic
- PMID: 19876913
- PMCID: PMC2862841
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25012
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-specific AKT1 is oncogenic
Erratum in
- Int J Cancer. 2012 Apr 15;130(8):1970
- Int J Cancer. 2012 Jun 15;130(12):E3
Abstract
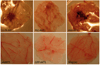
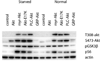
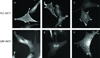
The protein kinase AKT1 (v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1), also referred to as protein kinase B (PKB), is an essential mediator of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. Elevated activity of AKT1 is common in human cancer. Localization at the plasma membrane, leading to enhanced phosphorylation and activation of AKT1, is an important factor determining the oncogenicity of this kinase. Although the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway is frequently upregulated in cancer, cancer-specific mutations in AKT1 are not common. Recently, such a mutation has been identified in breast, colon and ovarian cancers. The mutation is located in the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of AKT1 and results in a glutamic acid to lysine substitution at residue 17. The resultant change in the conformation of the PH domain facilitates membrane binding of the mutant protein. Here we show that exchange of the PH domain leading to preferential binding of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) over phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP(3)) constitutively activates AKT1. AKT1 with this altered PIP affinity induces oncogenic transformation in cultures of chicken embryo fibroblasts and causes neoplastic growth and angiogenesis in the chorioallantoic membrane of the chicken embryo. Gain-of-function mutants of AKT1 may not be affected by PI3K inhibitors that are currently in development. Therefore, AKT1 remains a distinct and important cancer target.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The GRP1 PH domain, like the AKT1 PH domain, possesses a sentry glutamate residue essential for specific targeting to plasma membrane PI(3,4,5)P(3).Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 15;50(45):9845-56. doi: 10.1021/bi2011306. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21932773 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of an oncogenic mutation that alters membrane targeting: Glu17Lys modifies the PIP lipid specificity of the AKT1 PH domain.Biochemistry. 2008 Nov 25;47(47):12260-9. doi: 10.1021/bi801683k. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18954143 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)trisphosphate in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-induced oncogenic transformation.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Jul;7(7):1132-8. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0068. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19584261 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of PI3K effector signalling in cancer by the phosphoinositide phosphatases.Biosci Rep. 2017 Feb 10;37(1):BSR20160432. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160432. Print 2017 Feb 28. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28082369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway.Science. 2002 May 31;296(5573):1655-7. doi: 10.1126/science.296.5573.1655. Science. 2002. PMID: 12040186 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles for AKT Isoform Preference in Cancer Progression Pathways.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Aug;19(8):1251-1257. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-1066. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33931488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GRP1 PH domain, like the AKT1 PH domain, possesses a sentry glutamate residue essential for specific targeting to plasma membrane PI(3,4,5)P(3).Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 15;50(45):9845-56. doi: 10.1021/bi2011306. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21932773 Free PMC article.
-
The Polarized Redistribution of the Contractile Vacuole to the Rear of the Cell is Critical for Streaming and is Regulated by PI(4,5)P2-Mediated Exocytosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 19;9:765316. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.765316. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35928786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer: Adaptive Responses, Drug Tolerance and Cellular Plasticity.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 26;13(7):1538. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071538. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33810522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt1 deletion prevents lung tumorigenesis by mutant K-ras.Oncogene. 2011 Apr 14;30(15):1812-21. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.556. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21242979 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

