Tai Chi is effective in treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 19877092
- PMCID: PMC3023169
- DOI: 10.1002/art.24832
Tai Chi is effective in treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of Tai Chi in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (OA) symptoms.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, single-blind, randomized controlled trial of 40 individuals with symptomatic tibiofemoral OA. Patients were randomly assigned to 60 minutes of Tai Chi (10 modified forms from classic Yang style) or attention control (wellness education and stretching) twice weekly for 12 weeks. The primary outcome was the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score at 12 weeks. Secondary outcomes included WOMAC function, patient and physician global assessments, timed chair stand, depression index, self-efficacy scale, and quality of life. We repeated these assessments at 24 and 48 weeks. Analyses were compared by intent-to-treat principles.
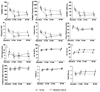
Results: The 40 patients had a mean age of 65 years and a mean body mass index of 30.0 kg/m(2). Compared with the controls, patients assigned to Tai Chi exhibited significantly greater improvement in WOMAC pain (mean difference at 12 weeks -118.80 mm [95% confidence interval (95% CI) -183.66, -53.94; P = 0.0005]), WOMAC physical function (-324.60 mm [95% CI -513.98, -135.22; P = 0.001]), patient global visual analog scale (VAS; -2.15 cm [95% CI -3.82, -0.49; P = 0.01]), physician global VAS (-1.71 cm [95% CI -2.75, -0.66; P = 0.002]), chair stand time (-10.88 seconds [95% CI -15.91, -5.84; P = 0.00005]), Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (-6.70 [95% CI -11.63, -1.77; P = 0.009]), self-efficacy score (0.71 [95% CI 0.03, 1.39; P = 0.04]), and Short Form 36 physical component summary (7.43 [95% CI 2.50, 12.36; P = 0.004]). No severe adverse events were observed.
Conclusion: Tai Chi reduces pain and improves physical function, self-efficacy, depression, and health-related quality of life for knee OA.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00362453.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tai Chi reduces pain and improves physical function for people with knee OA.J Physiother. 2010;56(1):57. doi: 10.1016/s1836-9553(10)70055-2. J Physiother. 2010. PMID: 20500138 No abstract available.
References
-
- Felson DT. Clinical practice. Osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:841–848. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence-based, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16:137–162. - PubMed
-
- Royal College of Physicians. URL: http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/CG059FullGuideline.pdf.
-
- van Baar ME, Dekker J, Lemmens JA, Oostendorp RA, Bijlsma JW. Pain and disability in patients with osteoarthritis of hip or knee: the relationship with articular, kinesiological, and psychological characteristics. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Slemenda C, Brandt KD, Heilman DK, et al. Quadriceps weakness and osteoarthritis of the knee. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:97–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

