miRNA control of tumor cell invasion and metastasis
- PMID: 19877123
- PMCID: PMC2950784
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25014
miRNA control of tumor cell invasion and metastasis
Abstract
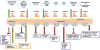
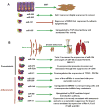
MicroRNAs have emerged as a novel class of noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-translational level in almost every biological event. A large body of evidence indicates that microRNAs regulate the expression of different genes that play an important role in cancer cell invasion, migration and metastasis. In this review, we briefly describe the role of various miRNAs in invasion, migration and metastasis which are essential steps during cancer progression.
Figures
References
-
- Vicente-Manzanares M, Webb DJ, Horwitz AR. Cell migration at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4917–9. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J, Condeelis J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:559–64. - PubMed
-
- Le Roy C, Wrana JL. Signaling and endocytosis: a team effort for cell migration. Dev Cell. 2005;9:167–8. - PubMed
-
- Pauley KM, Chan EK. MicroRNAs and their emerging roles in immunology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1143:226–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

