Synthetic mRNA splicing modulator compounds with in vivo antitumor activity
- PMID: 19877647
- PMCID: PMC2801547
- DOI: 10.1021/jm901215m
Synthetic mRNA splicing modulator compounds with in vivo antitumor activity
Abstract
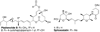
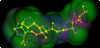
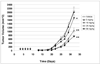
We report our progress on the development of new synthetic anticancer lead compounds that modulate the splicing of mRNA. We also report the synthesis and evaluation of new biologically active ester and carbamate analogues. Further, we describe initial animal studies demonstrating the antitumor efficacy of compound 5 in vivo. Additionally, we report the enantioselective and diastereospecific synthesis of a new 1,3-dioxane series of active analogues. We confirm that compound 5 inhibits the splicing of mRNA in cell-free nuclear extracts and in a cell-based dual-reporter mRNA splicing assay. In summary, we have developed totally synthetic novel spliceosome modulators as therapeutic lead compounds for a number of highly aggressive cancers. Future efforts will be directed toward the more complete optimization of these compounds as potential human therapeutics.
Figures

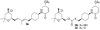
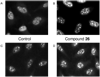


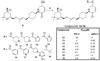

References
-
- Rymond B. Targeting the spliceosome. Nature Chemical Biology. 2007;3:533–535. - PubMed
-
- Kramer A. The structure and function of proteins involved in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:367–409. - PubMed
-
- Kaida D, Motoyoshi H, Tashiro E, Nojima T, Hagiwara M, Ishigami K, Watanabe H, Kitahara T, Yoshida T, Nakajima H, Tani T, Horinouchi S, Yoshida M. Spliceostatin A targets SF3b and inhibits both splicing and nuclear retention of pre-mRNA. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007;3:576–583. - PubMed
-
- Kotake Y, Sagane K, Owa T, Mimori-Kiyosue Y, Shimizu H, Uesugi M, Ishihama Y, Iwata M, Mizui Y. Splicing factor SF3b as a target of the antitumor natural product pladienolide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007;3:570–575. - PubMed
-
- Mizui Y, Sakai T, Iwata M, Uenaka T, Okamoto K, Shimizu H, Yamori T, Yoshimatsu K, Asada M. Pladienolides, new substances from culture of Streptomyces platensis Mer-11107. III. In vitro and in vivo antitumor activities. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2004;57:188–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

