Toward a model for Arf GTPases as regulators of traffic at the Golgi
- PMID: 19879269
- PMCID: PMC2787837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.066
Toward a model for Arf GTPases as regulators of traffic at the Golgi
Abstract
In this review, I summarize the likely roles played by ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) proteins in the regulation of membrane traffic at the Golgi, from the perspective of the GTPase. The most glaring limitations to the development of a coherent molecular model are highlighted; including incomplete information on the initiation of Arf activation, identification of the "accessory proteins" required for carrier maturation and scission, and those required for directed traffic and fusion at the destination membrane. Though incomplete, the molecular model of carrier biogenesis has developed rapidly in recent years and promises richness in understanding this essential process.
Figures

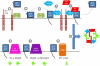
References
-
- Jekely G. Small GTPases and the evolution of the eukaryotic cell. Bioessays. 2003;25:1129–1138. - PubMed
-
- Dong JH, Wen JF, Tian HF. Homologs of eukaryotic Ras superfamily proteins in prokaryotes and their novel phylogenetic correlation with their eukaryotic analogs. Gene. 2007;396:116–124. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Kelly WG, Logsdon JM, Jr., Schurko AM, Harfe BD, Hill-Harfe KL, Kahn RA. Functional genomic analysis of the ADP-ribosylation factor family of GTPases: phylogeny among diverse eukaryotes and function in C. elegans. Faseb J. 2004;18:1834–1850. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SL, Wong SH, Hong W. The mammalian ARF-like protein 1 (Arl1) is associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Panic B, Whyte JR, Munro S. The ARF-like GTPases Arl1p and Arl3p Act in a Pathway that Interacts with Vesicle-Tethering Factors at the Golgi Apparatus. Curr Biol. 2003;13:405–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

