PI3 kinase signals BCR-dependent mature B cell survival
- PMID: 19879843
- PMCID: PMC2787092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.041
PI3 kinase signals BCR-dependent mature B cell survival
Abstract
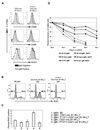
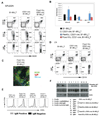
Previous work has shown that mature B cells depend upon survival signals delivered to the cells by their antigen receptor (BCR). To identify the molecular nature of this survival signal, we have developed a genetic approach in which ablation of the BCR is combined with the activation of specific, BCR dependent signaling cascades in mature B cells in vivo. Using this system, we provide evidence that the survival of BCR deficient mature B cells can be rescued by a single signaling pathway downstream of the BCR, namely PI3K signaling, with the FOXO1 transcription factor playing a central role.
Figures





References
-
- Aiba Y, Kameyama M, Yamazaki T, Tedder TF, Kurosaki T. Regulation of B-cell development by BCAP and CD19 through their binding to phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Blood. 2008;111:1497–1503. - PubMed
-
- Anzelon AN, Wu H, Rickert RC. Pten inactivation alters peripheral B lymphocyte fate and reconstitutes CD19 function. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:287–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

