Renal function in infants with sickle cell anemia: baseline data from the BABY HUG trial
- PMID: 19880138
- PMCID: PMC4755353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.06.060
Renal function in infants with sickle cell anemia: baseline data from the BABY HUG trial
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the feasibility and accuracy of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measurements in infants with sickle cell anemia (SCA).
Study design: The NHLBI/NICHD-sponsored Phase III randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial (BABY HUG) tests the hypothesis that hydroxyurea can prevent chronic organ damage in SCA. GFR elevation is a coprimary endpoint, measured quantitatively by technetium 99m-labeled diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) plasma clearance and estimated by the Schwartz equation with height and creatinine.
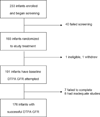
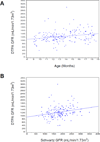
Results: Baseline DTPA GFR measurement was attempted in 191 infants; 176 of 184 completed studies (96%) were interpretable. Average age (mean +/- 1SD) was 13.7 +/- 2.6 months. Average DTPA GFR was 125.2 +/- 34.4 (range 40.2-300.9, normal 91.5 +/- 17.8 mL/min/1.73m(2)), while Schwartz estimates were higher at 184.4 +/- 55.5 mL/min/1.73m(2). DTPA GFR was correlated with Schwartz GFR (r(2) = 0.0658, P = .0012); also with age, weight, height, and kidney volume (all P < .002); but not with hemoglobin, HbF, white blood cell count, reticulocytes, medical events, or splenic function.
Conclusions: Quantitative GFR measurement is feasible but variable among infants with SCA. Schwartz GFR estimates are not highly correlated with quantitative DTPA GFR values. Baseline GFR measurements suggest that renal dysfunction in SCA, evidenced by glomerular hyperfiltration, begins during infancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Etteldorf JN, Smith JD, Tuttle AH, Diggs LW. Renal hemodynamic studies in adults with sickle cell anemia. Am J Med. 1955;18:243–248. - PubMed
-
- Whitten CF, Younes AA. A comparative study of renal concentrating ability in children with sickle cell anemia and in normal children. J Lab Clin Med. 1960;55:400–415. - PubMed
-
- Oster JR, Lespier LE, Lee SM, Pellegrini EL, Vaamonde CA. Renal acidification in sickle-cell disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1976;88:389–401. - PubMed
-
- Allon M. Renal abnormalities in sickle cell disease. Arch Intern Med. 1990;150:501–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HB-07150/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07160/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07153/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07156/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07157/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200023C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07152/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07155/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HB007160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07159/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HB007150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07158/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07151/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-07154/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

