Impact of medical Qigong on quality of life, fatigue, mood and inflammation in cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 19880433
- PMCID: PMC2826100
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdp479
Impact of medical Qigong on quality of life, fatigue, mood and inflammation in cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Substantial numbers of cancer patients use complementary medicine therapies, even without a supportive evidence base. This study aimed to evaluate in a randomized controlled trial, the use of Medical Qigong (MQ) compared with usual care to improve the quality of life (QOL) of cancer patients.
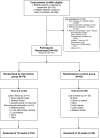
Patients and methods: One hundred and sixty-two patients with a range of cancers were recruited. QOL and fatigue were measured by Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Fatigue, respectively, and mood status by Profile of Mood State. The inflammatory marker serum C-reactive protein (CRP) was monitored serially.
Results: Regression analysis indicated that the MQ group significantly improved overall QOL (t(144) = -5.761, P < 0.001), fatigue (t(153) = -5.621, P < 0.001), mood disturbance (t(122) =2.346, P = 0.021) and inflammation (CRP) (t(99) = 2.042, P < 0.044) compared with usual care after controlling for baseline variables.
Conclusions: This study indicates that MQ can improve cancer patients' overall QOL and mood status and reduce specific side-effects of treatment. It may also produce physical benefits in the long term through reduced inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2007. edition. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2007.
-
- Chan C, Ho PS, Chow E. A body-mind-spirit model in health: an Eastern approach. Soc Work Health Care. 2001;34:261–282. - PubMed
-
- Miller M, Boyer MJ, Butow PN, et al. The use of unproven methods of treatment by cancer patients. Frequency, expectations and cost. Support Care Cancer. 1998;6:337–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous