Monitoring of donor chimerism in sorted CD34+ peripheral blood cells allows the sensitive detection of imminent relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 19880783
- PMCID: PMC2770975
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.007765
Monitoring of donor chimerism in sorted CD34+ peripheral blood cells allows the sensitive detection of imminent relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
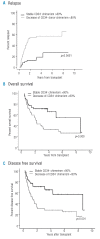
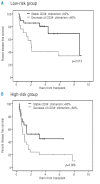
Analysis of donor chimerism is an important diagnostic tool to assess the risk of relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation, especially in patients lacking a specific marker suitable for monitoring of minimal residual disease. We prospectively investigated the predictive value of donor chimerism analyses in sorted CD34(+) peripheral blood cells in 90 patients with acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. The cumulative incidence of relapse after four years was significantly increased in cases with decreasing or incomplete CD34(+) donor chimerism (57% vs. 18%, p=0.0001). Multivariate analysis confirmed decreasing CD34(+) donor chimerism as an independent predictor of relapse and inferior survival. The interval between a decrease of CD34(+) chimerism of less than 80% and hematologic relapse was 61 days (range 0-567). Monitoring of CD34(+) donor chimerism in the peripheral blood allows prediction of imminent relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation even when a disease-specific marker is lacking.
Figures
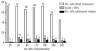
References
-
- Chang C, Storer BE, Scott BL, Bryant EM, Shulman HM, Flowers ME, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia arising from myelodysplastic syndrome: similar outcomes in patients with de novo disease and disease following prior therapy or antecedent hematologic disorders. Blood. 2007;110:1379–87. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tavernier E, Boiron JM, Huguet F, Bradstock K, Vey N, Kovacsovics T, et al. Outcome of treatment after first relapse in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia initially treated by the LALA-94 trial. Leukemia. 2007;21:1907–14. - PubMed
-
- Platzbecker U, Thiede C, Freiberg-Richter J, Helwig A, Mohr B, Prange G, et al. Treatment of relapsing leukemia after allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation by using dose-reduced conditioning followed by donor blood stem cells and GM-CSF. Ann Hematol. 2001;80:144–9. - PubMed
-
- Schmid C, Schleuning M, Aschan J, Ringden O, Hahn J, Holler E, et al. Low-dose ARAC, donor cells, and GM-CSF for treatment of recurrent acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2004;18:1430–3. - PubMed
-
- Schmid C, Schleuning M, Ledderose G, Tischer J, Kolb HJ. Sequential regimen of chemotherapy, reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem-cell transplantation, and prophylactic donor lymphocyte transfusion in high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5675–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

