Isolation and characterization of tirandamycins from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp
- PMID: 19883065
- PMCID: PMC2873692
- DOI: 10.1021/np9005597
Isolation and characterization of tirandamycins from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp
Abstract
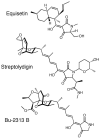
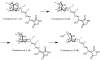
The novel dienoyl tetramic acids tirandamycin C (1) and tirandamycin D (2) with activity against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis were isolated from the marine environmental isolate Streptomyces sp. 307-9, which also produces the previously identified compounds tirandamycins A (3) and B (4). Spectroscopic analysis of 1 and 2 indicated structural similarity to 3 and 4, with differences only in the pattern of pendant oxygenation on the bicyclic ketal system. The isolation of these putative biosynthetic intermediates was enabled by their sequestration on an adsorbent resin during early stationary-phase fermentation.
Figures
References
-
- Royles BJL. Chem. Rev. 1995;95:1981–2001.
-
- Hazuda D, Blau CU, Felock P, Hastings J, Pramanik B, Wolfe A, Bushman F, Farnet C, Goetz M, Williams M, Silverman K, Lingham R, Singh S. Antiviral Chem. Chemother. 1999;10:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Holzapfel CW. Tetrahedron. 1968;24:2101–2119. - PubMed
-
- Rinehart KL, Beck JR, Borders DB, Epstein WW, Kinstle TH, Spicer LD, Krauss D, Button AC. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1963;161:346–348. - PubMed
-
- Crum GF, Devries WH, Eble TE, Large CM, Shell JW. Antibiot. Annu. 1955;3:893–896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases