A multiformalism and multiresolution modelling environment: application to the cardiovascular system and its regulation
- PMID: 19884187
- PMCID: PMC3034733
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2009.0163
A multiformalism and multiresolution modelling environment: application to the cardiovascular system and its regulation
Abstract
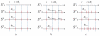
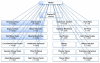
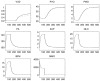
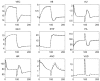
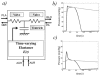
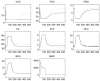
The role of modelling and simulation in the systemic analysis of living systems is now clearly established. Emerging disciplines, such as systems biology, and worldwide research actions, such as the Physiome Project or the Virtual Physiological Human, are based on an intensive use of modelling and simulation methodologies and tools. One of the key aspects in this context is to perform an efficient integration of various models representing different biological or physiological functions, at different resolutions, spanning through different scales. This paper presents a multiformalism modelling and simulation environment (M2SL) that has been conceived to ease model integration. A given model is represented as a set of coupled and atomic model components that may be based on different mathematical formalisms with heterogeneous structural and dynamical properties. A co-simulation approach is used to solve these hybrid systems. The pioneering model of the overall regulation of the cardiovascular system proposed by Guyton and co-workers in 1972 has been implemented under M2SL and a pulsatile ventricular model based on a time-varying elastance has been integrated in a multi-resolution approach. Simulations reproducing physiological conditions and using different coupling methods show the benefits of the proposed environment.
Figures




References
-
- Blackett SA, Bullivant D, Stevens C, Hunter PJ. Open source software infrastructure for computational biology and visualization. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005;6:6079–6080. - PubMed
-
- Defontaine A, Hernández A, Carrault G. Multi-formalism modelling of cardiac tissue. Lecture Notes in Computer Science - FIMH 2005. 2005;3504:394–403.
-
- Dou J, Xia L, Zhang Y, Shou G, Wei Q, Liu F, Crozier S. Mechanical analysis of congestive heart failure caused by bundle branch block based on an electromechanical canine heart model. Phys Med Biol. 2009;54:353–371. - PubMed
-
- Fenner JW, Brook B, Clapworthy G, Coveney PV, Feipel V, Gregersen H, Hose DR, Kohl P, Lawford P, McCormack KM, Pinney D, Thomas SR, Jan SVS, Waters S, Viceconti M. The europhysiome, step and a roadmap for the virtual physiological human. Philos Transact A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2008;366:2979–2999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
