SetDB1 contributes to repression of genes encoding developmental regulators and maintenance of ES cell state
- PMID: 19884255
- PMCID: PMC2779743
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1837309
SetDB1 contributes to repression of genes encoding developmental regulators and maintenance of ES cell state
Abstract
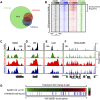
Transcription factors that play key roles in regulating embryonic stem (ES) cell state have been identified, but the chromatin regulators that help maintain ES cells are less well understood. A high-throughput shRNA screen was used to identify novel chromatin regulators that influence ES cell state. Loss of histone H3 Lys 9 (H3K9) methyltransferases, particularly SetDB1, had the most profound effects on ES cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled with massively parallel DNA sequencing (ChIP-Seq) and functional analysis revealed that SetDB1 and histone H3K9-methylated nucleosomes occupy and repress genes encoding developmental regulators. These SetDB1-occupied genes are a subset of the "bivalent" genes, which contain nucleosomes with H3K4me3 (H3K4 trimethylation) and H3K27me3 modifications catalyzed by Trithorax and Polycomb group proteins, respectively. These genes are subjected to repression by both Polycomb group proteins and SetDB1, and loss of either regulator can destabilize ES cell state.
Figures



References
-
- Ayyanathan K, Lechner MS, Bell P, Maul GG, Schultz DC, Yamada Y, Tanaka K, Torigoe K, Rauscher FJ., III Regulated recruitment of HP1 to a euchromatic gene induces mitotically heritable, epigenetic gene silencing: A mammalian cell culture model of gene variegation. Genes & Dev. 2003;17:1855–1869. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azuara V, Perry P, Sauer S, Spivakov M, Jorgensen HF, John RM, Gouti M, Casanova M, Warnes G, Merkenschlager M, et al. Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
