Exercise-induced histone modifications in human skeletal muscle
- PMID: 19884317
- PMCID: PMC2808551
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.181065
Exercise-induced histone modifications in human skeletal muscle
Abstract
Skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise confer many of the health benefits of physical activity and occur partly through alterations in skeletal muscle gene expression. The exact mechanisms mediating altered skeletal muscle gene expression in response to exercise are unknown. However, in recent years, chromatin remodelling through epigenetic histone modifications has emerged as a key regulatory mechanism controlling gene expression in general. The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of exercise on global histone modifications that mediate chromatin remodelling and transcriptional activation in human skeletal muscle in response to exercise. In addition, we sought to examine the signalling mechanisms regulating these processes. Following 60 min of cycling, global histone 3 acetylation at lysine 9 and 14, a modification associated with transcriptional initiation, was unchanged from basal levels, but was increased at lysine 36, a site associated with transcriptional elongation. We examined the regulation of the class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs), which are enzymes that suppress histone acetylation and have been implicated in the adaptations to exercise. While we found no evidence of proteasomal degradation of the class IIa HDACs, we found that HDAC4 and 5 were exported from the nucleus during exercise, thereby removing their transcriptional repressive function. We also observed activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in response to exercise, which are two kinases that induce phosphorylation-dependent class IIa HDAC nuclear export. These data delineate a signalling pathway that might mediate skeletal muscle adaptations in response to exercise.
Figures
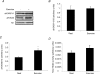
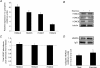
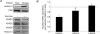
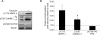
Comment in
-
Exercise-induced histone acetylation - playing tag with the genome.J Physiol. 2010 Mar 15;588(Pt 6):905-6. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.185595. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20231147 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fischle W, Dequiedt F, Hendzel MJ, Guenther MG, Lazar MA, Voelter W, Verdin E. Enzymatic activity associated with class II HDACs is dependent on a multiprotein complex containing HDAC3 and SMRT/N-CoR. Mol Cell. 2002;9:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Hutber CA, Hardie DG, Winder WW. Electrical stimulation inactivates muscle acetyl-CoA carboxylase and increases AMP-activated protein kinase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 1997;272:E262–E266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

