In vitro and in vivo activities of 1-hydroxy-2-alkyl-4(1H)quinolone derivatives against Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 19884369
- PMCID: PMC2798484
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01001-09
In vitro and in vivo activities of 1-hydroxy-2-alkyl-4(1H)quinolone derivatives against Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
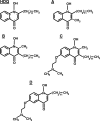
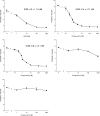
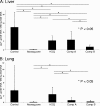
1-Hydroxy-2-dodecyl-4(1H)quinolone (HDQ) was recently identified as a Toxoplasma gondii inhibitor. We describe here two novel 1-hydroxyquinolones, which displayed 50% inhibitory concentrations 10- and 5-fold lower than that of HDQ. In a mouse model of acute toxoplasmosis, these two compounds and HDQ reduced the percentages of infected peritoneal cells and decreased the parasite loads in lungs and livers. Compound B showed a tendency toward lowering parasite loads in brains in a mouse model of toxoplasmic encephalitis.
Figures

References
-
- Bustamante, C., C. N. Batista, and M. Zalis. 2009. Molecular and biological aspects of antimalarial resistance in Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Curr. Drug Targets 10:279-290. - PubMed
-
- Dunay, I. R., M. M. Heimesaat, F. N. Bushrab, R. H. Müller, H. Stocker, K. Arasteh, M. Kurowski, R. Fitzner, K. Borner, and O. Liesenfeld. 2004. Atovaquone maintenance therapy prevents reactivation of toxoplasmic encephalitis in a murine model of reactivated toxoplasmosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:4848-4854. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

