MicroRNAs in cancer: small molecules with a huge impact
- PMID: 19884536
- PMCID: PMC2793003
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.0317
MicroRNAs in cancer: small molecules with a huge impact
Abstract
Every cellular process is likely to be regulated by microRNAs, and an aberrant microRNA expression signature is a hallmark of several diseases, including cancer. MicroRNA expression profiling has indeed provided evidence of the association of these tiny molecules with tumor development and progression. An increasing number of studies have then demonstrated that microRNAs can function as potential oncogenes or oncosuppressor genes, depending on the cellular context and on the target genes they regulate. Here we review our current knowledge about the involvement of microRNAs in cancer and their potential as diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

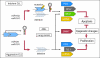
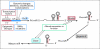

References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Pekarsky Y, Santanam U, Cimmino A, et al. Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11590–11593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

