High risk of recurrence for patients with breast cancer who have human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive, node-negative tumors 1 cm or smaller
- PMID: 19884543
- PMCID: PMC2792998
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.2025
High risk of recurrence for patients with breast cancer who have human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive, node-negative tumors 1 cm or smaller
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the risk of recurrence in women diagnosed with T1a and T1b, node-negative, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) -positive breast cancer.
Methods: We reviewed 965 T1a,bN0M0 breast cancers diagnosed at our institution between 1990 and 2002. Dedicated breast pathologists confirmed HER2 positivity if 3+ by immunohistochemistry or if it had a ratio of 2.0 or greater by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy or trastuzumab were excluded. Kaplan-Meier product was used to calculate recurrence-free survival (RFS) and distant recurrence-free survival (DRFS). Cox proportional hazard models were fit to determine associations between HER2 status and survival after adjustment for patient and disease characteristics. Additionally, 350 breast cancers from two other institutions were used for validation.
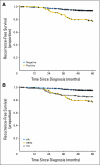
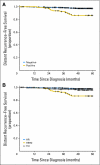
Results: Ten percent of patients had HER2-positive tumors. At a median follow-up of 74 months, there were 72 recurrences. The 5-year RFS rates were 77.1% and 93.7% in patients with HER2-positive and HER2-negative tumors, respectively (P < .001). The 5-year DRFS rates were 86.4% and 97.2% in patients with HER2-positive and HER2-negative tumors, respectively (P < .001). In multivariate analysis, patients with HER2-positive tumors had higher risks of recurrence (hazard ratio [HR], 2.68; 95% CI, 1.44 to 5.0; P = .002) and distant recurrence (HR, 5.3; 95% CI, 2.23 to 12.62; P < .001) than those with HER2-negative tumors. Patients with HER2-positive tumors had 5.09 times (95% CI, 2.56 to 10.14; P < .0001) the rate of recurrences and 7.81 times (95% CI, 3.17 to 19.22; P < .0001) the rate of distant recurrences at 5 years compared with patients who had hormone receptor-positive tumors.
Conclusion: Patients with HER2-positive T1abN0M0 tumors have a significant risk of relapse and should be considered for systemic, anti-HER2, adjuvant therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Refining therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: T stands for trastuzumab, tumor size, and treatment strategy.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec 1;27(34):5671-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.2222. Epub 2009 Nov 2. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19884535 No abstract available.
-
Breast cancer: disentangling the intricate web.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jun 10;28(17):e281; author reply e282-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.6634. Epub 2010 Apr 5. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20368535 No abstract available.
-
Beyond HER2 and trastuzumab: heterogeneity, systems biology, and cancer origin research may guide the future for personalized treatment of very early but aggressive breast cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jun 10;28(17):e279-80; author reply e282-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.7061. Epub 2010 Apr 20. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20406920 No abstract available.
References
-
- Buzdar AU, Ibrahim NK, Francis D, et al. Significantly higher pathologic complete remission rate after neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab, paclitaxel, and epirubicin chemotherapy: Results of a randomized trial in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3676–3685. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, et al. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–712. - PubMed
-
- Ravdin PM, Chamness GC. The c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene as a prognostic and predictive marker in breast cancer: A paradigm for the development of other macromolecular markers—A review. Gene. 1995;159:19–27. - PubMed
-
- Joensuu H, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P-L, Bono P, et al. Adjuvant docetaxel or vinorelbine with or without trastuzumab for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:809–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

