The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucuronopyranoside on Gastritis and Reflux Esophagitis in Rats
- PMID: 19885013
- PMCID: PMC2766707
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.4.295
The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucuronopyranoside on Gastritis and Reflux Esophagitis in Rats
Abstract
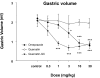
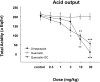
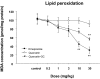
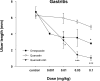
It was evaluated the inhibitory action of quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside (QGC) on reflux esophagitis and gastritis in rats. QGC was isolated from the herba of Rumex Aquaticus. Reflux esophagitis or gastritis was induced surgically or by administering indomethacin, respectively. Oral QGC decreased ulcer index, injury area, gastric volume, and acid output and increased gastric pH as compared with quercetin. Furthermore, QGC significantly decreased gastric lesion sizes induced by exposing the gastric mucosa to indomethacin. Malondialdehyde levels were found to increase significantly after inducing reflux esophagitis, and were reduced by QGC, but not by quercetin or omeprazole. These results show that QGC can inhibit reflux esophagitis and gastritis in rats.
Keywords: Gastritis; Lipid peroxidation; Quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside; Reflux esophagitis.
Figures


References
-
- Alvarez A, Pomar F, Sevilla, Montero MJ. Gastric antisecretory and antiulcer activities of an ethanolic extract of Bidens pilosa L. var. radiata Schult. Bip. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;67:333–340. - PubMed
-
- Bell NJ, Burget D, Howden CW, Wilkinson J, Hunt H. Appropriate acid suppression for the management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Digestion. 1992;51(Suppl 1):59–67. - PubMed
-
- Biancani P, Sohn UD, Rich HG, Harnett KM, Behar J. Signal transduction pathways in esophageal and lower esophageal sphincter circular muscle. Am J Med. 1997;103:23S–28S. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid, sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed

