Intrapartum tenofovir and emtricitabine reduces low-concentration drug resistance selected by single-dose nevirapine for perinatal HIV prevention
- PMID: 19886836
- PMCID: PMC2828257
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2009.0088
Intrapartum tenofovir and emtricitabine reduces low-concentration drug resistance selected by single-dose nevirapine for perinatal HIV prevention
Abstract
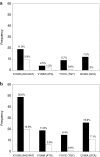
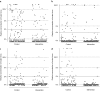
A single dose of tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) during labor significantly reduces peripartum nevirapine-associated viral drug resistance when measured by consensus HIV sequencing. It is unknown whether this effect extends to HIV subpopulations of <25-50%. We conducted a randomized trial of single-dose TDF/FTC added to peripartum nevirapine to reduce drug resistance associated with nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). To detect mutations for NNRTIs comprising > or = 2% of the viral population, we used an oligonucleotide ligation assay (OLA) at codons 103, 106, 181, and 190 of HIV reverse transcriptase. To assess development of drug resistance mutations to our study intervention, OLA was also performed at codons 65 and 184. Among the 328 women included in the 2-week analysis, those receiving TDF/FTC were less likely to have NNRTI resistance by OLA (RR = 0.40, 95% CI = 0.21-0.77). A similar trend was observed among the 315 women included in the 6-week analysis (RR = 0.45, 95% CI = 0.31-0.66). Only two (1%) specimens had detectable K65R by OLA. Both were at 6 weeks postpartum; one was detected in the intervention arm and one in the control arm (p = 0.96). M184V was not detected. The ability of single-dose TDF/FTC to protect against peripartum NVP-induced NNRTI resistance extends to minority populations. This efficacy is achieved without significant selection of TDF- or FTC-resistant viruses.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00204308.
Figures


References
-
- Eshleman SH. Mracna M. Guay LA, et al. Selection and fading of resistance mutations in women and infants receiving nevirapine to prevent HIV-1 vertical transmission (HIVNET 012) AIDS. 2001;15:1951–1957. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro RL. Thior I. Gilbert PB, et al. Maternal single-dose nevirapine versus placebo as part of an antiretroviral strategy to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission in Botswana. AIDS. 2006;20:1281–1288. - PubMed
-
- Jourdain G. Ngo-Giang-Huong N. Le Coeur S, et al. Intrapartum exposure to nevirapine and subsequent maternal responses to nevirapine-based antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:229–240. - PubMed
-
- Cressey TR. Jourdain G. Lallemant MJ, et al. Persistence of nevirapine exposure during the postpartum period after intrapartum single-dose nevirapine in addition to zidovudine prophylaxis for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;38:283–288. - PubMed
-
- McIntyre J. Martinson N. Gray G, et al. Addition of short-course combivir (CBV) to single dose viramune (sdNVP) for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission (pMTCT) of HIV-1 can significantly decrease the development of maternal and paediatric NNRTI-resistant virus; In the 3rd IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis and Treatment; Rio de Janiero, Brazil. 24–27 July; 2005. [Abstract TuFo0204].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

