Plasticity in Ca2+ selectivity of Orai1/Orai3 heteromeric channel
- PMID: 19887627
- PMCID: PMC2780800
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907714106
Plasticity in Ca2+ selectivity of Orai1/Orai3 heteromeric channel
Abstract
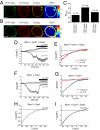
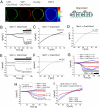
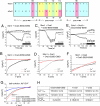
A general cellular response following depletion of intracellular calcium stores involves activation of store-operated channels (SOCs). While Orai1 forms the native Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channel in mast and T cells, the molecular architecture of less Ca(2+) selective SOCs is insufficiently defined. Here we present evidence that diminished Ca(2+) selectivity and robust Cs(+) permeation together with a reduced fast inactivation are characteristics of heteromeric Orai1 and Orai3 channels in contrast to their homomeric forms. The first extracellular loop of these Orai isoforms differs by two aspartates replacing glutamates that affect the selectivity. Co-expression of an Orai3 mutant that mimicked the first loop of Orai1 with either Orai1 or Orai3 recovered or decreased Ca(2+) selectivity, respectively. Heteromeric Orai1/3 protein assembly provides a concept for less Ca(2+)-selective SOCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

