Electrical characteristics of rat skeletal muscle in immaturity, adulthood and after sciatic nerve injury, and their relation to muscle fiber size
- PMID: 19887721
- PMCID: PMC2821572
- DOI: 10.1088/0967-3334/30/12/009
Electrical characteristics of rat skeletal muscle in immaturity, adulthood and after sciatic nerve injury, and their relation to muscle fiber size
Abstract
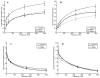
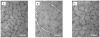
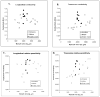
Localized impedance methods can provide useful approaches for assessing neuromuscular disease. The mechanism of these impedance changes remains, however, uncertain. In order to begin to understand the relation of muscle pathology to surface impedance values, 8 immature rats, 12 mature rats and 8 mature rats that had undergone sciatic crush were killed. Measurement was made on tissue from the gastrocnemius muscle from each animal in an impedance cell, and the conductivity and relative permittivity of the tissue were calculated in both the longitudinal and transverse directions for frequencies of 2 kHz to 1 MHz. In addition, quantitative histological analysis was performed on the tissue. Significant elevations in transverse conductivity and transverse relative permittivity were found with animal growth, but longitudinal values showed no difference. After sciatic crush, both transverse and longitudinal conductivity increased significantly, with no change in the relative permittivity in either direction. The frequency dependence of the values also changed after nerve injury. In the healthy animals, there was a strong linear relation between measured conductivity and relative permittivity with cell area, but not for the sciatic crush animals. These results provide a first step toward developing a comprehensive understanding of how the electrical properties of muscle alter in neuromuscular disease states.
Figures
References
-
- Baumann SB, Wozny DR, Kelly SK, Meno FM. The electrical conductivity of human cerebrospinal fluid at body temperature. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1997;44:220–3. - PubMed
-
- Epstein BR, Foster KR. Anisotropy in the dielectric properties of skeletal muscle. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1983;21:51–5. - PubMed
-
- Dubowtiz V. Muscle biopsy: a practical approach. 2. Balliere Tindal; Philadephelia: 1985. p. 29.
-
- Esper GJ, Shiffman CA, Aaron R, Lee KS, Rutkove SB. Muscle Nerve. Vol. 34. 2006. Assessing neuromuscular disease with multifrequency electrical impedance myography; pp. 595–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
