Main immunogenic region structure promotes binding of conformation-dependent myasthenia gravis autoantibodies, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor conformation maturation, and agonist sensitivity
- PMID: 19890000
- PMCID: PMC2787250
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2833-09.2009
Main immunogenic region structure promotes binding of conformation-dependent myasthenia gravis autoantibodies, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor conformation maturation, and agonist sensitivity
Abstract
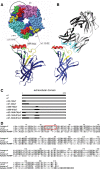
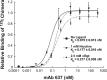
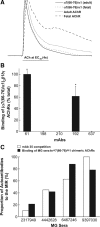
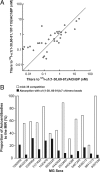
The main immunogenic region (MIR) is a conformation-dependent region at the extracellular apex of alpha1 subunits of muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) that is the target of half or more of the autoantibodies to muscle AChRs in human myasthenia gravis and rat experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. By making chimeras of human alpha1 subunits with alpha7 subunits, both MIR epitopes recognized by rat mAbs and by the patient-derived human mAb 637 to the MIR were determined to consist of two discontiguous sequences, which are adjacent only in the native conformation. The MIR, including loop alpha1 67-76 in combination with the N-terminal alpha helix alpha1 1-14, conferred high-affinity binding for most rat mAbs to the MIR. However, an additional sequence corresponding to alpha1 15-32 was required for high-affinity binding of human mAb 637. A water soluble chimera of Aplysia acetylcholine binding protein with the same alpha1 MIR sequences substituted was recognized by a majority of human, feline, and canine myasthenia gravis sera. The presence of the alpha1 MIR sequences in alpha1/alpha7 chimeras greatly promoted AChR expression and significantly altered the sensitivity to activation. This reveals a structural and functional, as well as antigenic, significance of the MIR.
Figures



References
-
- Beroukhim R, Unwin N. Three-dimensional location of the main immunogenic region of the acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1995;15:323–331. - PubMed
-
- Castelán F, Mulet J, Aldea M, Sala S, Sala F, Criado M. Cytoplasmic regions adjacent to the M3 and M4 transmembrane segments influence expression and function of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. A study with single amino acid mutants. J Neurochem. 2007;100:406–415. - PubMed
-
- Castillo M, Mulet J, Aldea M, Gerber S, Sala S, Sala F, Criado M. Role of the N-terminal α-helix in biogenesis of α7 nicotinic receptors. J Neurochem. 2009;108:1399–1409. - PubMed
-
- Colman A. Transcription and translation: a practical approach. In: Hames BD, Higgins SJ, editors. Practical approach series. Oxford, UK: IRL Press; 1984. pp. 271–302.
-
- Conroy WG, Saedi MS, Lindstrom J. TE671 cells express an abundance of a partially mature acetylcholine receptor α subunit which has characteristics of an assembly intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:21642–21651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
