EGFR regulates the expression of keratinocyte-derived granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 19890352
- PMCID: PMC7322627
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2009.336
EGFR regulates the expression of keratinocyte-derived granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
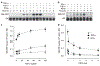
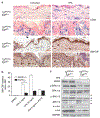
Recent advances in the knowledge of the EGFR pathway have revealed its contribution to distinct immune/inflammatory functions of the epidermis. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the role of EGFR in the regulation of keratinocyte GM-CSF expression. In cultured human keratinocytes, proinflammatory cytokines synergized with TGF-alpha to induce GM-CSF expression. Accordingly, high epidermal levels of EGFR activation are associated with enhanced expression of GM-CSF in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis or allergic contact dermatitis. In cultured keratinocytes, pharmacological inhibition of EGFR activity reduced GM-CSF promoter transactivation, whereas genetic inhibition of AP-1 reduced expression of GM-CSF. Furthermore, EGFR activation enhanced TNF-alpha-induced c-Jun phosphorylation and DNA binding, whereas c-Jun silencing reduced GM-CSF expression. Using two different mouse models, we showed that the lack of a functional EGFR pathway was associated with reduced cytokine-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK1/2, c-Jun and reduced keratinocyte-derived GM-CSF expression both in vitro and in vivo. Finally, the analysis of GM-CSF expression in the skin of cancer patients treated with anti EGFR drugs showed an association between ERK activity, c-Jun phosphorylation, and epidermal GM-CSF expression. These data demonstrate that the EGFR pathway is critical for the upregulation of keratinocyte GM-CSF expression under conditions of cytokine stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author states no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abdul Rhaman JA, Moodley YP, Phillips MJ (2004) Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis associated with psoriasis and complicated by mycobacterial infection: successful treatment with granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor after a partial response to whole lavage. Respirology 9:419–22 - PubMed
-
- Bonifati C, Carducci M, Cordiali Fei P, Trento E, Sacerdoti G, Fazio M et al. (1994) Correlated increases of TNF-α, IL-6 and GM-CSF levels in suction blister fluids and sera of psoriatic patients-relation with disease severity. Clin Exp Dermatol 19:383–7 - PubMed
-
- Braunstein S, Kaplan G, Gottlieb AB, Schwartz M, Walsh G, Abalos RM et al. (1994) GM-CSF activates regenerative epidermal growth and stimulates proliferation in human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 103:601–4 - PubMed
-
- Breuhahn K, Mann A, Müller G, Wilhelmi A, Schirmacher P, Enk A et al. (2000) Epidermal overexpression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor induces keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ 11:111–21 - PubMed
-
- Cianfarani F, Tommasi R, Failla CM, Viviano MT, Annessi G, Papi M et al. (2006) Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor treatment of human chronic ulcers promotes angiogenesis associated with de novo vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in the ulcer bed. Br J Dermatol 154:34–41 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

