Dysregulation of macrophage signal transduction by Toxoplasma gondii: past progress and recent advances
- PMID: 19891610
- PMCID: PMC2774889
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01122.x
Dysregulation of macrophage signal transduction by Toxoplasma gondii: past progress and recent advances
Abstract
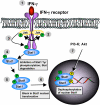
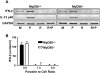
The opportunistic protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii is well known as a strong inducer of cell-mediated immunity, largely as a result of proinflammatory cytokine induction during in vivo infection. Yet, during intracellular infection the parasite suppresses signal transduction pathways leading to these proinflammatory responses. The opposing responses are likely to reflect the parasite's need to stimulate immunity allowing host survival and parasite persistence, and at the same time avoiding excessive responses that could result in parasite elimination and host immunopathology. This Review summarizes past and present investigations into the effects of Toxoplasma on host cell signal transduction. These studies reveal insight into the profound suppression of proinflammatory cytokine responses that occurs when the parasite infects macrophages and other cells of innate immunity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
From cells to signaling cascades: manipulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Dec 5;39(3):193-203. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00279-7. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14642303 Review.
-
Role of macrophage-derived cytokines in the induction and regulation of cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;219:127-39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-51014-4_12. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8791695 Review. No abstract available.
-
Forward genetics screens using macrophages to identify Toxoplasma gondii genes important for resistance to IFN-γ-dependent cell autonomous immunity.J Vis Exp. 2015 Mar 12;(97):52556. doi: 10.3791/52556. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 25867017 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii virulence effectors.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Nov;10(11):766-78. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2858. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23070557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma and Dendritic Cells: An Intimate Relationship That Deserves Further Scrutiny.Trends Parasitol. 2019 Nov;35(11):870-886. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Trends Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31492624 Review.
Cited by
-
Innate immunity to Toxoplasma gondii infection.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Feb;14(2):109-21. doi: 10.1038/nri3598. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24457485 Review.
-
Insights into inflammatory bowel disease using Toxoplasma gondii as an infectious trigger.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;90(7):668-75. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.93. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22064707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of activation-associated host cell gene expression by the apicomplexan parasite Theileria annulata.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Sep;14(9):1434-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01809.x. Epub 2012 May 23. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22533473 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Toxoplasma gondii genotype and absence of host MAL/Myd88 on the temporal regulation of gene expression in infected microglial cells.Exp Parasitol. 2011 Dec;129(4):409-13. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2011.08.016. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Exp Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21924265 Free PMC article.
-
SAG2A protein from Toxoplasma gondii interacts with both innate and adaptive immune compartments of infected hosts.Parasit Vectors. 2013 Jun 5;6:163. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-163. Parasit Vectors. 2013. PMID: 23735002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 2004;363:1965–76. - PubMed
-
- Dunn JD, Butcher BA, Denkers EY, Boothroyd JC. Alterations in host cell-biology due to Toxoplasma gondii. In: Weiss LM, Kim K, editors. Toxoplasma gondii: the model apicomplexan. Academic Press; Amsterdam: 2007. pp. 317–40.
-
- Pepper M, Hunter CA. Innate immune recognition and regulation of protective immunity to Toxoplasma gondii. In: Ajioka JW, Soldati D, editors. Toxoplasma: Molecular and Cellular Biology. Horizon Bioscience; Norfolk: 2007. pp. 111–26.
-
- Debierre-Grockiego F, Campos MA, Azzouz N, et al. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by glycosylphosphatidylinositols derived from Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 2007;179:1129–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

