Generation of lung epithelial-like tissue from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 19891764
- PMCID: PMC2777141
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-105
Generation of lung epithelial-like tissue from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Human embryonic stem cells (hESC) have the capacity to differentiate in vivo and in vitro into cells from all three germ lineages. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of specific culture conditions on the differentiation of hESC into lung epithelial cells.
Methods: Undifferentiated hESC, grown on a porous membrane in hESC medium for four days, were switched to a differentiation medium for four days; this was followed by culture in air-liquid interface conditions during another 20 days. Expression of several lung markers was measured by immunohistochemistry and by quantitative real-time RT-PCR at four different time points throughout the differentiation and compared to appropriate controls.
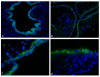
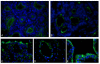
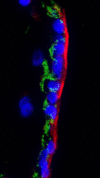
Results: Expression of CC16 and NKX2.1 showed a 1,000- and 10,000- fold increase at day 10 of differentiation. Other lung markers such as SP-C and Aquaporin 5 had the highest expression after twenty days of culture, as well as two markers for ciliated cells, FOXJ1 and beta-tubulin IV. The results from qRT-PCR were confirmed by immunohistochemistry on paraffin-embedded samples. Antibodies against CC16, SP-A and SP-C were chosen as specific markers for Clara Cells and alveolar type II cells. The functionality was tested by measuring the secretion of CC16 in the medium using an enzyme immunoassay.
Conclusion: These results suggest that by using our novel culture protocol hESC can be differentiated into the major cell types of lung epithelial tissue.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

