Peripheral peptide YY inhibits propulsive colonic motor function through Y2 receptor in conscious mice
- PMID: 19892938
- PMCID: PMC2806102
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00349.2009
Peripheral peptide YY inhibits propulsive colonic motor function through Y2 receptor in conscious mice
Abstract
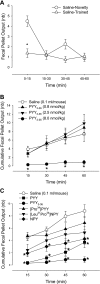
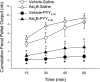
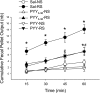
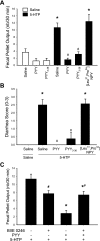
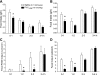
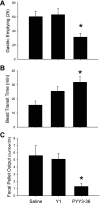
Peptide YY (PYY) antisecretory effect on intestinal epithelia is well established, whereas less is known about its actions to influence colonic motility in conscious animals. We characterized changes in basal function and stimulated colonic motor function induced by PYY-related peptides in conscious mice. PYY(3-36), PYY, and neuropeptide Y (NPY) (8 nmol/kg) injected intraperitoneally inhibited fecal pellet output (FPO) per hour during novel environment stress by 90%, 63%, and 57%, respectively, whereas the Y(1)-preferring agonists, [Pro(34)]PYY and [Leu(31),Pro(34)]NPY, had no effect. Corticotrophin-releasing factor 2 receptor antagonist did not alter PYY(3-36) inhibitory action. PYY and PYY(3-36) significantly reduced restraint-stimulated defecation, and PYY(3-36) inhibited high-amplitude distal colonic contractions in restrained conscious mice for 1 h, by intraluminal pressure with the use of a microtransducer. PYY suppression of intraperitoneal 5-hydroxytryptophan induced FPO and diarrhea was blocked by the Y(2) antagonist, BIIE0246, injected intraperitoneally and mimicked by PYY(3-36), but not [Leu(31),Pro(34)]NPY. PYY(3-36) also inhibited bethanechol-stimulated FPO and diarrhea. PYY(3-36) inhibited basal FPO during nocturnal feeding period and light phase in fasted/refed mice for 2-3 h, whereas the reduction of food intake lasted for only 1 h. PYY(3-36) delayed gastric emptying after fasting-refeeding by 48% and distal colonic transit time by 104%, whereas [Leu(31),Pro(34)]NPY had no effect. In the proximal and distal colon, higher Y(2) mRNA expression was detected in the mucosa than in muscle layers, and Y(2) immunoreactivity was located in nerve terminals around myenteric neurons. These data established that PYY/PYY(3-36) potently inhibits basal and stress/serotonin/cholinergic-stimulated propulsive colonic motor function in conscious mice, likely via Y(2) receptors.
Figures
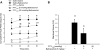
Similar articles
-
Peptide YY, neuropeptide Y and corticotrophin-releasing factor modulate gastrointestinal motility and food intake during acute stress.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014 Nov;26(11):1605-14. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12428. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014. PMID: 25238483
-
Endogenous peptide YY and neuropeptide Y inhibit colonic ion transport, contractility and transit differentially via Y₁ and Y₂ receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):471-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01401.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21457230 Free PMC article.
-
NPY Y2 receptor agonist PYY(3-36) inhibits diarrhea by reducing intestinal fluid secretion and slowing colonic transit in mice.Peptides. 2010 Apr;31(4):671-5. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.11.005. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 19925840
-
Peptide YY(1-36) and peptide YY(3-36): Part I. Distribution, release and actions.Obes Surg. 2006 May;16(5):651-8. doi: 10.1381/096089206776944959. Obes Surg. 2006. PMID: 16687037 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y and peptide YY: major modulators of gastrointestinal blood flow and function.Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):G701-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.5.G701. Am J Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1659217 Review.
Cited by
-
Appetite- and Weight-Regulating Neuroendocrine Circuitry in Hypothalamic Obesity.Endocr Rev. 2024 May 7;45(3):309-342. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad033. Endocr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38019584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance to early-life stress in mice: effects of genetic background and stress duration.Front Behav Neurosci. 2011 Apr 4;5:13. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00013. eCollection 2011. Front Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21519375 Free PMC article.
-
Enteroendocrine cells regulate intestinal homeostasis and epithelial function.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2024 Nov 1;593:112339. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2024.112339. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39111616 Review.
-
Peripheral activation of the Y2-receptor promotes secretion of GLP-1 and improves glucose tolerance.Mol Metab. 2013 Mar 14;2(3):142-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.03.001. eCollection 2013. Mol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24049729 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic injection of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist mecamylamine affects licking, eyelid size, and locomotor and autonomic activities but not temporal prediction in male mice.Mol Brain. 2022 Sep 6;15(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13041-022-00959-y. Mol Brain. 2022. PMID: 36068635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams SH, Won WB, Schonhoff SE, Leiter AB, Paterniti JR., Jr Effects of peptide YY[3–36] on short-term food intake in mice are not affected by prevailing plasma ghrelin levels. Endocrinology 145: 4967–4975, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Arantes RM, Nogueira AM. Distribution of enteroglucagon- and peptide YY-immunoreactive cells in the intestinal mucosa of germ-free and conventional mice. Cell Tissue Res 290: 61–69, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniam A. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) family of hormones: progress in the development of receptor selective agonists and antagonists. Curr Pharm Des 9: 1165–1175, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Batterham RL, Cowley MA, Small CJ, Herzog H, Cohen MA, Dakin CL, Wren AM, Brynes AE, Low MJ, Ghatei MA, Cone RD, Bloom SR. Gut hormone PYY(3–36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature 418: 650–654, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Browning KN, Lees GM. Inhibitory effects of NPY on ganglionic transmission in myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig descending colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 12: 33–41, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

