A route to brightly fluorescent carbon nanotubes for near-infrared imaging in mice
- PMID: 19893526
- PMCID: PMC2834239
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2009.294
A route to brightly fluorescent carbon nanotubes for near-infrared imaging in mice
Abstract
The near-infrared photoluminescence intrinsic to semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes is ideal for biological imaging owing to the low autofluorescence and deep tissue penetration in the near-infrared region beyond 1 microm. However, biocompatible single-walled carbon nanotubes with high quantum yield have been elusive. Here, we show that sonicating single-walled carbon nanotubes with sodium cholate, followed by surfactant exchange to form phospholipid-polyethylene glycol coated nanotubes, produces in vivo imaging agents that are both bright and biocompatible. The exchange procedure is better than directly sonicating the tubes with the phospholipid-polyethylene glycol, because it results in less damage to the nanotubes and improves the quantum yield. We show whole-animal in vivo imaging using an InGaAs camera in the 1-1.7 microm spectral range by detecting the intrinsic near-infrared photoluminescence of the 'exchange' single-walled carbon nanotubes at a low dose (17 mg l(-1) injected dose). The deep tissue penetration and low autofluorescence background allowed high-resolution intravital microscopy imaging of tumour vessels beneath thick skin.
Figures
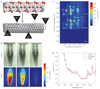

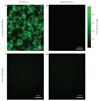

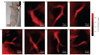
Comment in
-
Bioimaging: second window for in vivo imaging.Nat Nanotechnol. 2009 Nov;4(11):710-1. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.326. Nat Nanotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19898521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Z, Winters M, Holodniy M, Dai HJ. siRNA delivery into human T cells and primary cells with carbon-nanotube transporters. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:2023–2027. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, et al. In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nature Nanotech. 2007;2:47–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

