IKK/NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation-mediated tumour promotion and metastasis
- PMID: 19893576
- PMCID: PMC2799209
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.243
IKK/NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation-mediated tumour promotion and metastasis
Abstract
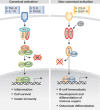
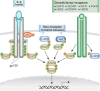
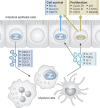
Our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that link inflammation and cancer has significantly increased in recent years. Here, we analyse genetic evidence indicating that the transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) have a central role in this context by regulating distinct functions in cancer cells and surrounding non-tumorigenic cells. In immune cells, NF-kappaB induces the transcription of genes that encode pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can act in a paracrine manner on initiated cells. By contrast, in tumorigenic cells, both NF-kappaB and STAT3 control apoptosis, and STAT3 can also enhance proliferation. Consequently, inflammation should be considered as a valuable target for cancer prevention and therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B (2009) Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res 15: 425–430 - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357: 539–545 - PubMed
-
- Becker C et al. (2004) TGF-β suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 21: 491–501 - PubMed
-
- Bollrath J et al. (2009) gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 15: 91–102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

