An insight into the biochemistry of inborn errors of metabolism for a clinical neurologist
- PMID: 19893643
- PMCID: PMC2771954
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-2327.41873
An insight into the biochemistry of inborn errors of metabolism for a clinical neurologist
Abstract
Neurological dysfunction is an important manifestation of inherited metabolic disorders. Although these are more common in childhood, adult onset forms with a different clinical presentation are often encountered. Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions have substantially improved the outcome in many of these conditions. This makes it essential that the practicing physician be familiar with the clinical presentation and diagnosis of these disorders. For the evaluation of a patient with a possible inborn error of metabolism, simple screening tests may aid in the diagnosis and provide direction for more comprehensive laboratory analysis. In this review, we present a practical approach to diagnosis of neurometabolic disorders. Establishing a specific diagnosis in these disorders will enable the clinician in offering a definitive long-term treatment, prognosis and genetic counselling.
Keywords: Biochemical tests; diagnosis; inborn errors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

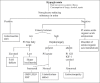

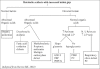

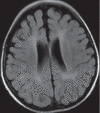

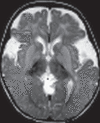

References
-
- Garrod AG. Inborn error of metabolism. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1909.
-
- Scriver CR, Beaud, Sly WS, Valle D, et al., editors. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001.
-
- Clarke JT, editor. A clinical guide to inherited metabolic diseases. 2nd ed. United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 2002.
-
- Shevell M, Ashwal S, Donley D, Flint J, Gingold M, Hirtz D, et al. Practice parameter: Evaluation of the child with global developmental delay: Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the practice committee of the child neurology society. Neurology. 2003;60:367–80. - PubMed
-
- Burton BK. Inborn errors of metabolism in infancy: A guide to diagnosis. Pediatrics. 1998;102:e63. - PubMed

